Figure 1: Neuropeptide control of puberty and its metabolic regulation.
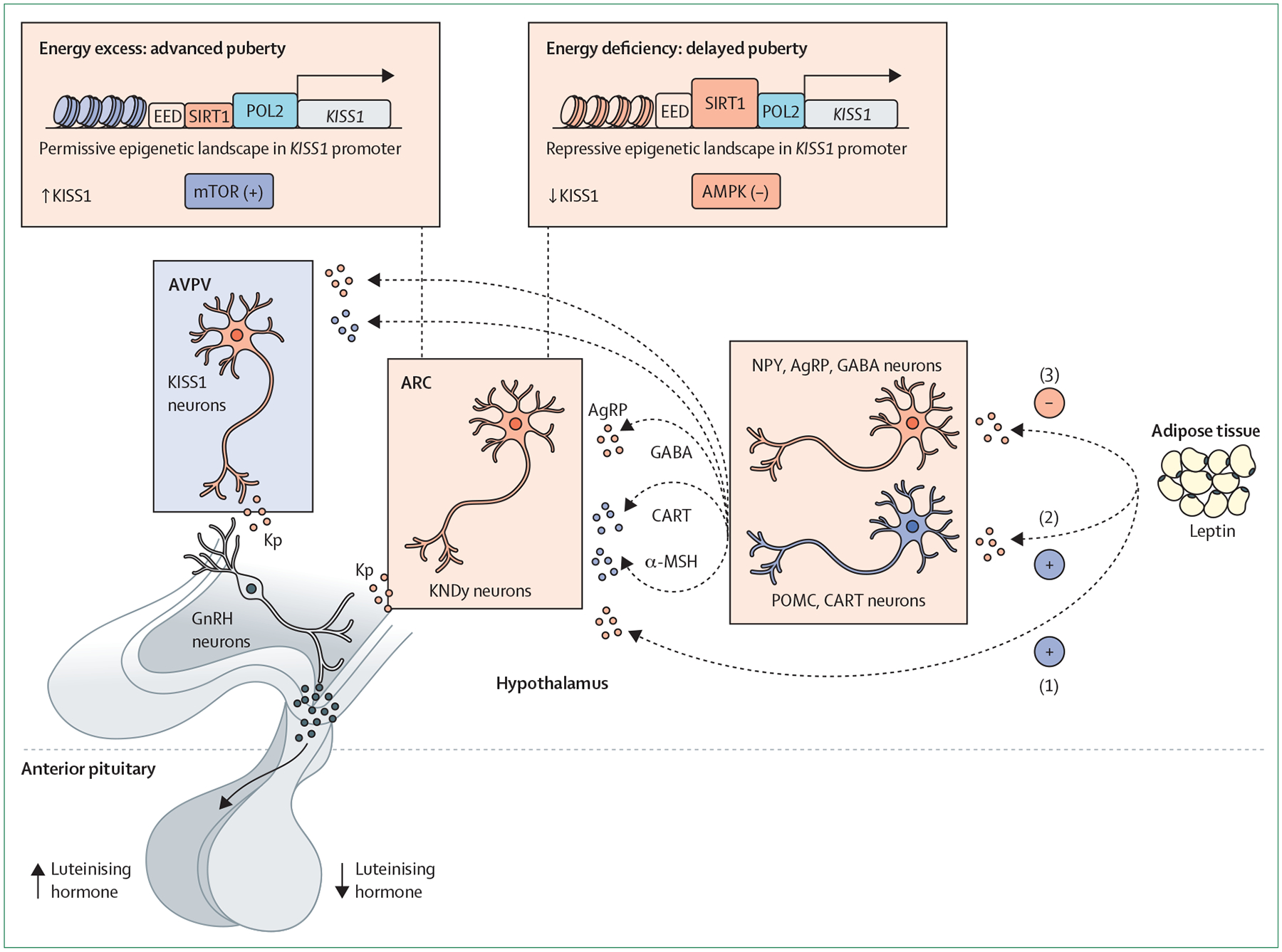
Schematic presentation of populations of Kiss1 neurons at the two main hypothalamic areas, namely the ARC and AVPV, and related hypothalamic neuronal pathways and cellular energy sensors involved in the physiological control of puberty. Related neuronal pathways seemingly include neurons producing NPY and AgRP, and neurons expressing POMC and CART neurons. These pathways participate in transmitting the modulatory actions of key metabolic hormones, such as leptin. Three possible modes of action of leptin are presented: (1) direct excitatory actions on Kiss1 neurons; (2) indirect excitatory actions via POMC neurons; and (3) indirect inhibitory actions on NPY/AgRP neurons. In addition, these circuits convey the influence of conditions of energy deficit, which result in delayed puberty (denoted by low luteinising hormone levels), and situations of energy excess (obesity), that advance pubertal onset (denoted by high luteinising hormone levels). Cellular energy sensors and metabolic mediators involved in this process include mTOR, AMPK and SIRT1. AgRP=agouti-related protein. AMPK=adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase. ARC=arcuate nucleus. AVPV=anteroventral periventricular nucleus. CART=cocaine-regulated and amphetamine-regulated transcript. EED=embryonic ectoderm development (component of polycomb repressive complex 2). GABA=γ-aminobutyric acid. GnRH=gonadotropin-releasing hormone. KNDy=kisspeptin, neurokinin B, and dynorphin. Kp=kisspeptin. MSH=melanocyte-stimulating hormone. mTOR=mammalian target of rapamycin. NPY=neuropeptide Y. POL2=RNA polymerase 2. POMC=proopiomelanocortin. SIRT1=sirtuin 1.
