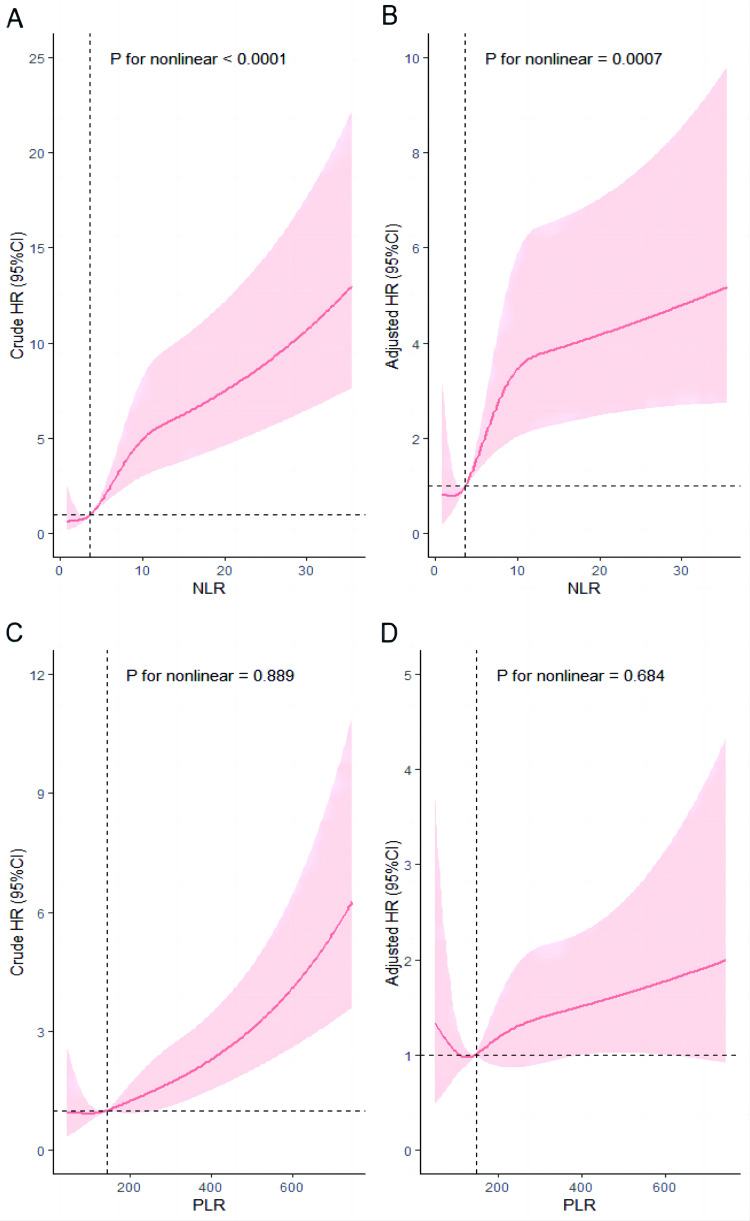
Figure 2.
Dose-response relationship between NLR, PLR and in-hospital mortality in elderly patients with AMI from RCS analysis. (A) Unadjusted dose-response relationship between NLR and in-hospital mortality in elderly patients with AMI; (B) Adjusted dose-response relationship between NLR and in-hospital mortality in elderly patients with AMI; (C) Unadjusted dose-response relationship between PLR and in-hospital mortality in elderly patients with AMI; (D) Adjusted dose-response relationship between PLR and in-hospital mortality in elderly patients with AMI. Adjusted factors include: sex, BMI, diabetes, type of AMI, heart failure, eGFR, CTNI, CK-MB, Aspirin use and Statins use.
Abbreviations: NLR, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; PLR, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio; AMI acute myocardial infarction. RCS, restricted cubic splines; BMI, body mass index; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; CTNI, cardiac troponin I; CK-MB creatine kinase-MB.