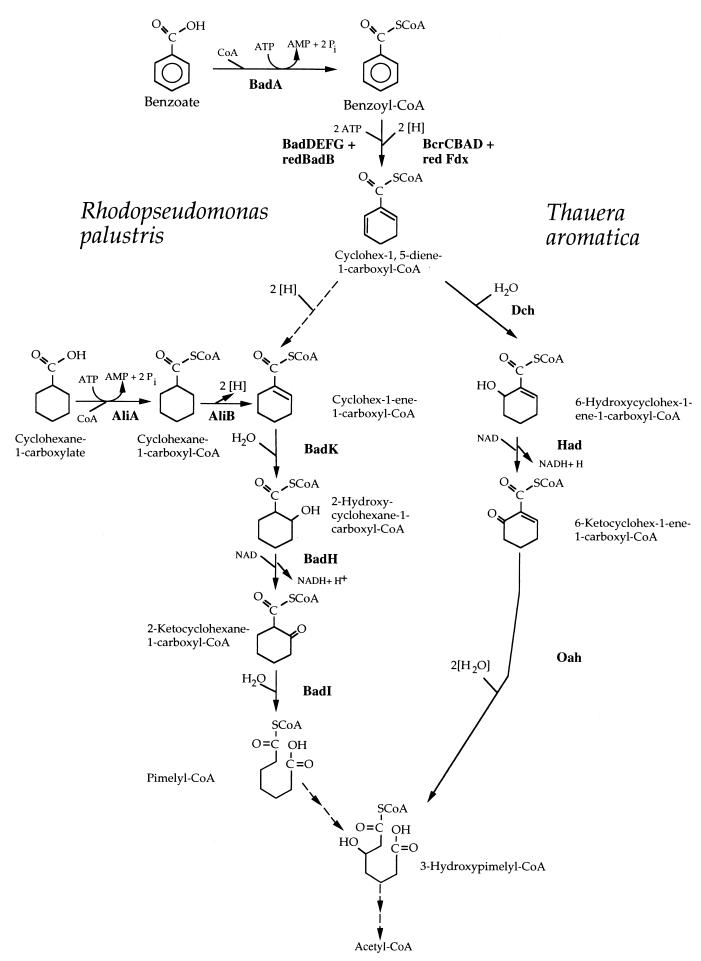
FIG. 1.
Comparison of anaerobic benzoate degradation by R. palustris and T. aromatica. Reactions involved in funneling cyclohexanecarboxylate into the anaerobic benzoate degradation pathway in R. palustris are shown. Solid arrows indicate enzymatic activities that have been purified from either R. palustris or T. aromatica (1, 6, 11, 23, 25, 26, 33). Dashed arrows indicate hypothetical enzymatic reactions. Assignment of gene products from R. palustris (Fig. 2) and T. aromatica (7) to specific steps is indicated. redBadB, reduced BadB; redFdx, reduced ferredoxin.