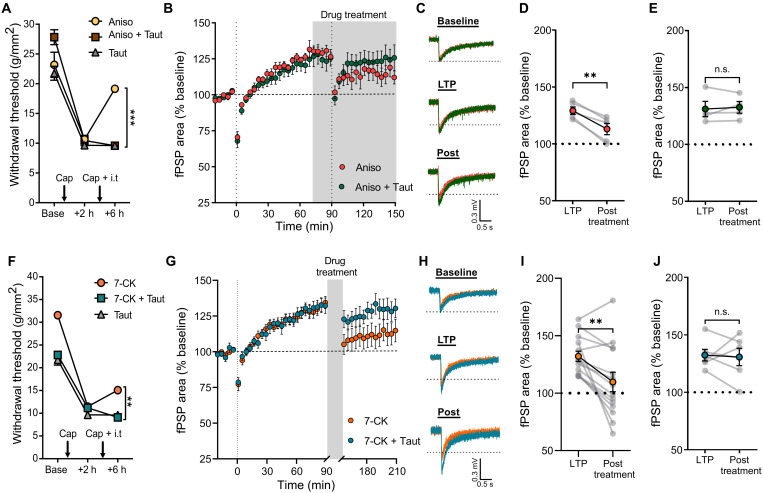
Fig. 3. Anisomycin and 7-CK induce the reversal of hyperalgesia and dorsal horn LTP via PP1-dependent mechanism.
(A) Intrathecal injection of tautomycetin (Taut; PP1 inhibitor) prevented the reversal of hyperalgesia by reactive destabilization. (B) After LTP induction, bath application of anisomycin (Aniso; red) or Aniso + Taut (green) at 75 min was followed by a second round of 2-Hz stimulation onto dorsal roots at 90 min. (C) Representative traces of fPSPs recorded at baseline, 90 min (LTP), and 150 min (Post). (D and E) fPSPs area compared before (LTP) and after (posttreatment) 2-Hz reactivation of potentiated pathways in the presence of (D) Aniso or (E) Aniso + Taut. (F) PP1 inhibition prevented the reversal of hyperalgesia by NI-NMDAR signaling. (G) Reversal of LTP by bath application of 7-CK (orange) and dorsal root stimulation was not observed when tautomycetin was applied with 7-CK (turquoise). (H) Representative traces of fPSPs recorded at baseline, 90 min (LTP), and 210 min (post). (I and J) fPSP area compared before (LTP) and after (posttreatment) administration of (I) 7-CK or (J) 7-CK + Taut. Data are means ± SEM. n.s., P > 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.