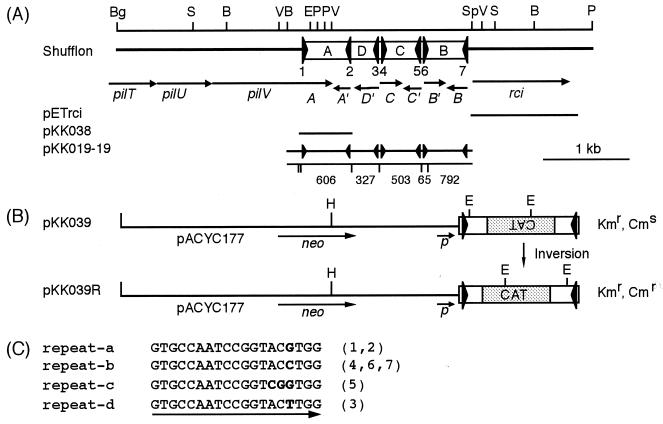
FIG. 1.
(A) Gene organization of pilTUV, shf, and rci regions of plasmid R64. This figure represents an arrangement (corresponding to pKK010-85) of many isomers of the shufflon subjected to multiple DNA inversions. At the top, a restriction map is shown. B, BstBI; Bg, BglII; E, EcoRI; P, PstI; S, SspI; Sp, SphI; V, EcoRV. The large triangles represent the 19-bp repeat sequences. Open reading frames deduced from the nucleotide sequence are represented by arrows. The lines indicate the DNA portions present in various plasmids. Below pKK019-19, HaeIII sites and the lengths (in base pairs) of DNA fragments produced by HaeIII and SspI digestion of pKK019-19 are indicated by vertical lines and numbers, respectively (see Fig. 5A). (B) DNA substrate for Rci-mediated recombination. The open bars represent segment A of the R64 shufflon. The large triangles represent the 19-bp sequences. The stippled bars indicate a DNA fragment carrying the promoterless CAT gene. The lines represent the pACYC177 sequence. (C) Four types of seven 19-bp repeat sequences. The numbers in parentheses correspond to the numbers of the 19-bp repeat sequences represented in panel A. Nucleotides that differ from the other sequences are indicated by boldface letters.