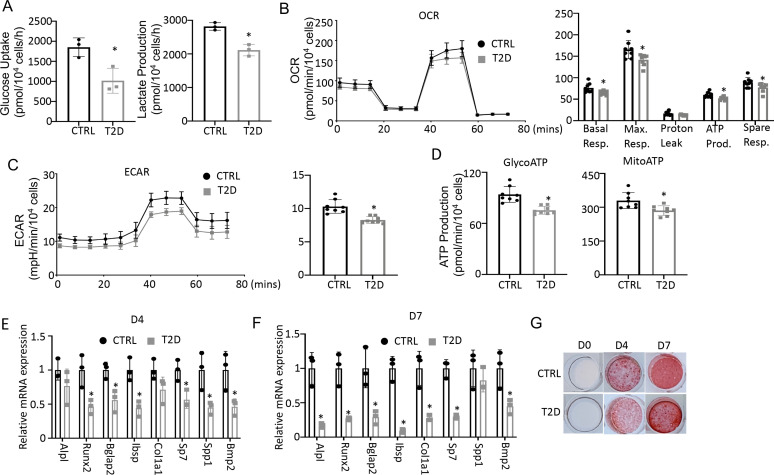
Figure 5. Type 2 diabetes (T2D) impairs glucose metabolism and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC).
(A) Glucose uptake and lactate production rates. n=3. (B, C) Seahorse measurements of oxygen consumption rate (OCR) (B) and extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) (C). n=8. (D) Projected ATP production glycolysis (glycoATP) and mitochondria (mitoATP) based on Seahorse. n=8. (E, F) qPCR for osteoblast markers at day 4 (E) and day 7 (F) of differentiation. n=3. (G) Alizarin red staining. Data presented as mean ± SD. *p<0.05, Unpaired student’s t-test.