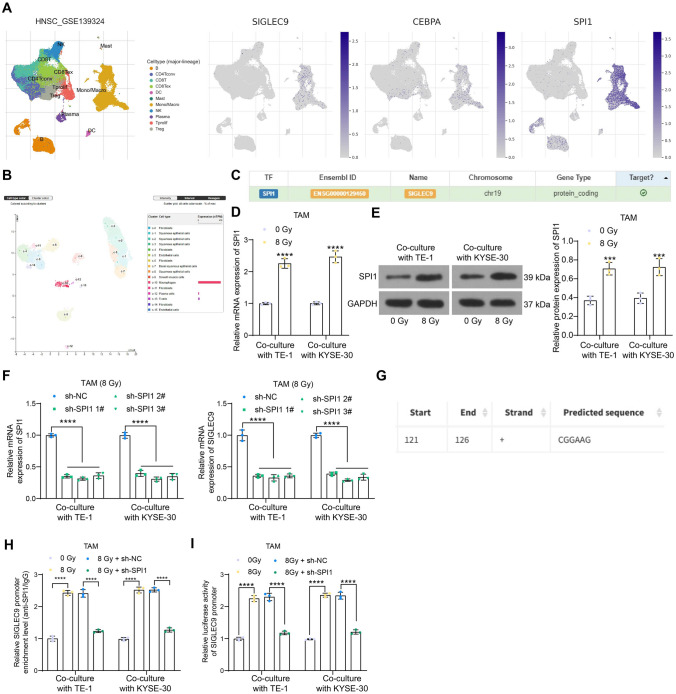
Fig. 4.
SPI1 is upregulated in high-dose irradiation-exposed TAMs and activates SIGLEC9 transcription. a, expression of transcription factors in different types of immune cells in HNSC analyzed by single-cell analysis; b, expression of CEBPA and SPI1 in esophagus analyzed by single-cell analysis; c, SPI1 predicted as a candidate upstream regulator of SIGLEC9; d-e, mRNA and protein expression of SPI1 in high-dose irradiation-exposed TAMs analyzed by qPCR (d) and WB (e) analyses; f, SPI1 and SIGLEC9 mRNA in TAMs pre-transfected with sh-SPI1 analyzed by qPCR analysis; g, putative binding site of SPI1 to SIGLEC9 promoter; h, binding of SIGLEC9 promoter with SPI1 in TAMs upon high-dose irradiation treatment and sh-SPI1 transfection analyzed by ChIP-qPCR assay; i, transcription activity of SIGLEC9 promoter in TAMs upon high-dose irradiation treatment and sh-SPI1 transfection analyzed by luciferase assay. Differences of the normally distributed data between groups were analyzed by two-way ANOVA (d, e, f, h and i). Significance of difference was analyzed by Sidak's multiple comparisons test (d and e), Dunnett's multiple comparisons test (f) and Tukey's multiple comparisons test (h and i). ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001