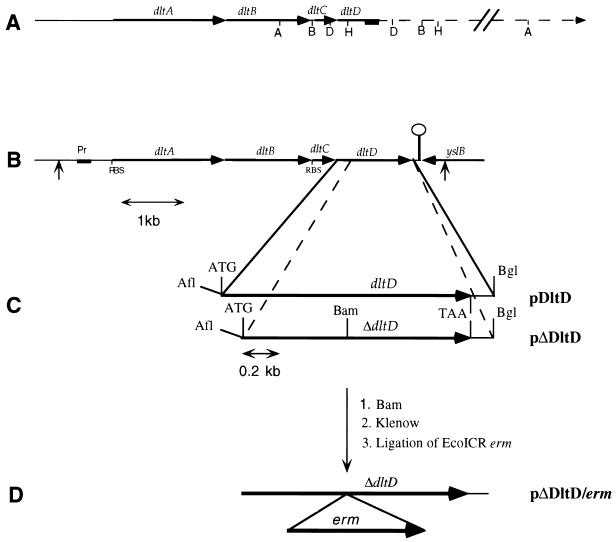
FIG. 1.
Cloning strategy for the isolation, expression, insertional inactivation, and complementation of dltD. (A) L. rhamnosus chromosomal map of dltD and flanking regions. The site of probe hybridization to dltD is shown by the solid box. (B) Physical map of the L. rhamnosus dlt operon. ORFs are shown by arrows, and the terminator of transcription is shown by ○. The positions of primers for the amplification of the dlt operon and its cloning into pNZ123 are shown by vertical arrows. (C) Inserts containing dltD and ΔdltD in pET-3d, designated pDltD and pΔDltD. The AflIII and BglII sites were introduced by PCR with the mutagenic primers described in Materials and Methods. (D) Cloning of the EcoICR erm fragment from pVE6006 into the BamHI site of ΔdltD to obtain the plasmid (pΔDltD/erm) for insertional inactivation. Pr, promoter; RBS, ribosome binding site; ATG, start codon; TAA, termination codon; A, AvaI; B, BalI; D, DraI; H, HincII, Afl, AflIII; Bam, BamHI; Bgl, BglII.