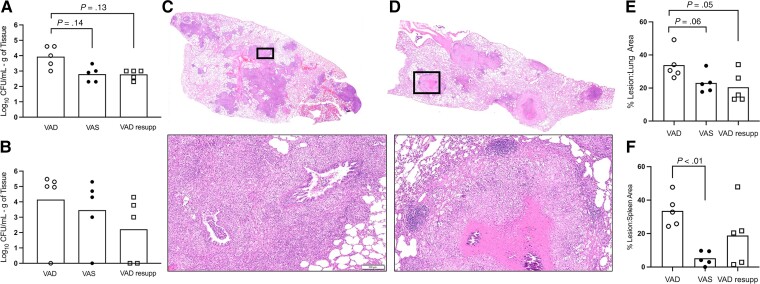
Figure 2.
Impact of vitamin A deficiency on tuberculosis disease outcome in the guinea pig model 60 days after infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Shown are outcomes from VAD (open circle), VAS (closed circle), and VAD guinea pigs resupplemented with vitamin A at 30 days after infection (open square). A, Bacterial burden in lung of VAD, VAS, and VAD resupp. B, Bacterial burden in spleen of VAD, VAS, and VAD resupp. C, Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)–stained histology images of a full lung section from a VAD guinea pig. D, Representative H&E-stained histology images of a full lung section from a VAD guinea pig. Black boxes outline the high magnification images below panels C and D (bar = 100 μm). E, Proportion of lung tissue area affected by inflammatory lesions in VAD, VAS, and VAD resupp guinea pigs. F, Proportion of spleen tissue area affected by inflammatory lesions in VAD, VAS, and VAD resupp guinea pigs. Abbreviations: CFU, colony-forming unit; resupp, resupplemented; VAD, vitamin A deficient; VAS, vitamin A sufficient.