Table 3.
Adjusted OR and 95 % CI for healthy eating markers prevalence in high and medium categories of economic residential segregation; MOVE-se Academias study, Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2014–2015
| Regular consumption of fruit | Regular consumption of vegetables | Regular consumption of beans | Regular consumption of fish | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95 % CI | P value | OR | 95 % CI | P value | OR | 95 % CI | P value | OR | 95 % CI | P value | |
| Unadjusted | ||||||||||||
| High | 0·59 | 0·40, 0·88 | 0·009 | 0·43 | 0·26, 0·70 | 0·001 | 2·00 | 1·17, 3·41 | 0·011 | 0·58 | 0·39, 0·87 | 0·008 |
| Medium | 0·57 | 0·41, 0·81 | 0·002 | 0·48 | 0·30, 0·75 | 0·001 | 1·19 | 0·77, 1·83 | 0·428 | 0·57 | 0·41, 0·81 | 0·002 |
| Low | 1·00 | Ref. | – | 1·00 | Ref. | – | 1·00 | Ref. | – | 1·00 | Ref. | – |
| Model 1 | ||||||||||||
| High | 0·68 | 0·45, 1·03 | 0·068 | 0·49 | 0·31, 0·79 | 0·004 | 2·02 | 1·18, 3·48 | 0·010 | 0·63 | 0·42, 0·94 | 0·025 |
| Medium | 0·62 | 0·43, 0·89 | 0·009 | 0·54 | 0·35, 0·84 | 0·006 | 1·23 | 0·79, 1·90 | 0·353 | 0·60 | 0·42, 0·85 | 0·005 |
| Low | 1·00 | Ref. | – | 1·00 | Ref. | – | 1·00 | v | 1·00 | Ref. | – | |
| Model 2 | ||||||||||||
| High | 0·84 | 0·55, 1·28 | 0·426 | 0·60 | 0·37, 0.96 | 0·034 | 1·84 | 1·07, 3·18 | 0·026 | 0·72 | 0·48, 1·10 | 0·136 |
| Medium | 0·70 | 0·49, 1·01 | 0·059 | 0·64 | 0·42, 0·98 | 0·040 | 1·23 | 0·79, 1·91 | 0·351 | 0·66 | 0·46, 0·94 | 0·024 |
| Low | 1·00 | Ref. | – | 1·00 | Ref. | – | 1·0 | Ref. | – | 1·00 | Ref. | – |
| Model 3 | ||||||||||||
| High | 0·86 | 0·56, 1·32 | 0·492 | 0·61 | 0·39, 0·99 | 0·044 | 1·82 | 1·06, 3·12 | 0·030 | 0·74 | 0·49, 1·12 | 0·159 |
| Medium | 0·71 | 0·49, 1·03 | 0·075 | 0·63 | 0·42, 0·97 | 0·038 | 1·23 | 0·79, 1·90 | 0·353 | 0·65 | 0·46, 0·94 | 0·022 |
| Low | 1·00 | Ref. | – | 1·00 | Ref. | – | 1·00 | Ref. | – | 1·00 | Ref. | – |
| Model 4 | ||||||||||||
| High | 0·84 | 0·55, 1·30 | 0·443 | 0·62 | 0·39, 0·98 | 0·043 | 1·85 | 1·07, 3·19 | 0·026 | 0·73 | 0·48, 1·10 | 0·141 |
| Medium | 0.71 | 0·49, 1·03 | 0·071 | 0·64 | 0·42, 0·97 | 0·038 | 1·23 | 0·79, 1·91 | 0·344 | 0·65 | 0·45, 0·94 | 0·020 |
| Low | 1·00 | Ref. | – | 1·00 | Ref. | – | 1·00 | Ref. | – | 1·00 | Ref. | – |
Ref., reference category.
Logistic regression models using the generalized estimating equations method were used to estimate adjusted OR and 95 % CI. Residential segregation was included in models as a categorical variable with ‘low’ residential segregation as the reference category (high, 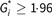 ; medium:
; medium: 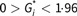 ; and low,
; and low, 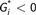 ). Regular consumption defined as a consumption of any amount for five days or more per week, except for fish (one or more days per week). Low perceived food environments were considered when the answers to all questions about fruit and vegetable availability (variety, quality and price) were ‘no’.
). Regular consumption defined as a consumption of any amount for five days or more per week, except for fish (one or more days per week). Low perceived food environments were considered when the answers to all questions about fruit and vegetable availability (variety, quality and price) were ‘no’.
Model 1: adjusted for age, gender and skin colour.
Model 2: Model 1 + family income and education.
Model 3: Model 2 + self-rated health and BMI (kg/m2).
Model 4: Model 3 + low perceived food environment.
Bold denotes statistical significance, P < 0·05.
