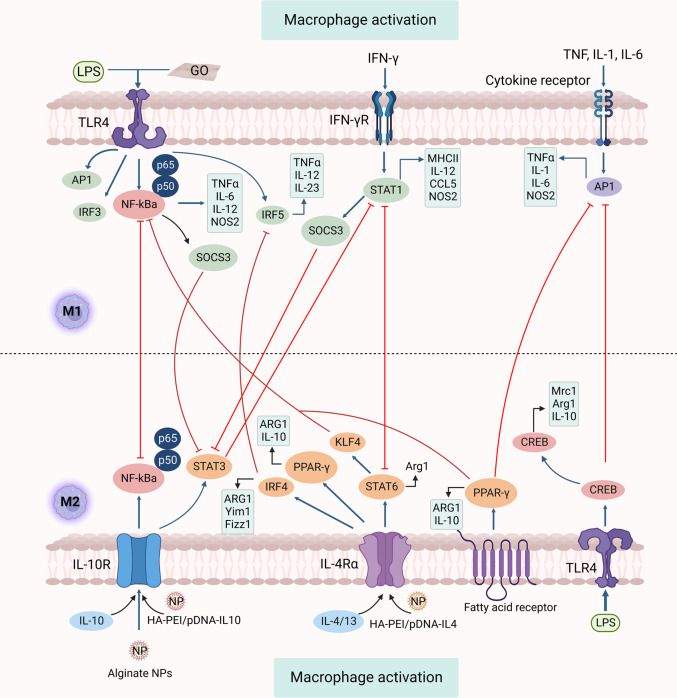
Fig. 1.
Pathways for signaling macrophage polarization. The figure demonstrates numerous strategies essential for macrophage polarization and depicts feedback control on signaling pathways of M1 and M2. Key signal channels include IRFs, STATs, NF-κB, and SOCS. The downstream protein STAT6 is krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF-4). Also, macrophage polarization can be induced by GO (graphene oxide) towards the M1 phenotype. HA-PEI/pDNA-IL-10 or HA-PEI/pDNA-IL-4 NPs) and tuftsin-modified alginate NPs containing murine cytokine IL-10 plasmid DNA modulate programming from M1 toward M2. Similarly, enhanced expression of API, PPARγ, and CREB is mediated by cytokine receptor, fatty acid receptor, and TLR4, respectively. STAT1-STAT6 introduces the feedback control of M1 and M2, IRF5-IRF4, NF-κB-PPARγ, AP1-CREB, and AP1-PPARγ, which play a crucial role in inflammatory disease instigation, development, and termination. TLR toll-like receptor, CREB cyclic AMP-responsive element binding, NF-κB nuclear factor kappa light chain enhancer of activated B cells, STAT signal transducers and activators of transcription, PPARγ peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ, IRF interferon regulatory transcription factor, API apigenin