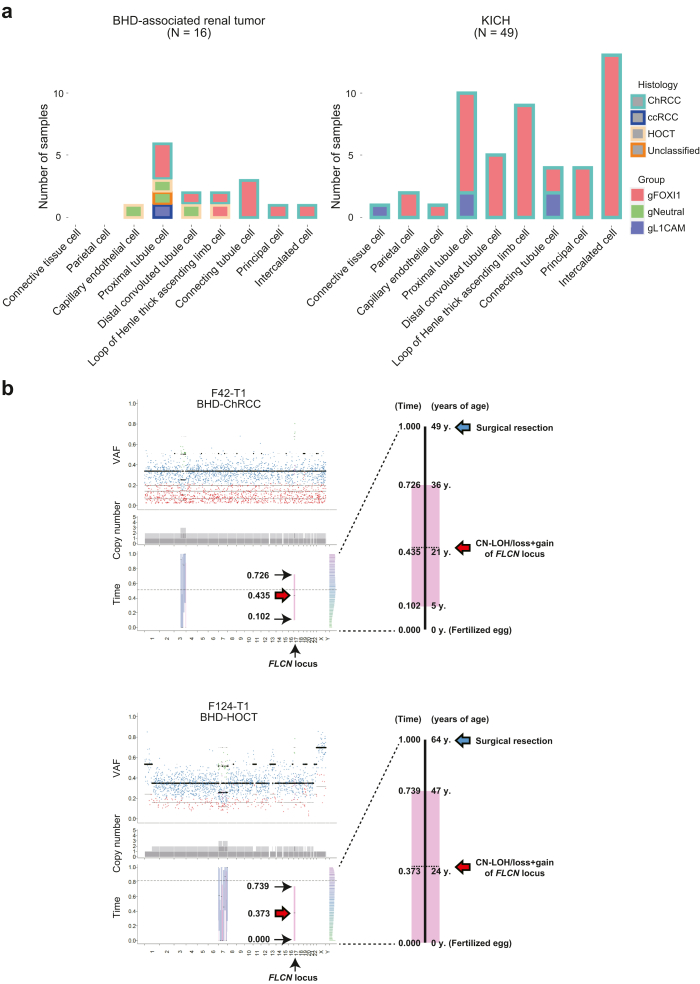
Fig. 5.
Bioinformatic algorithms depict natural history of BHD-associated renal tumourigenesis. (a) The bar plots show putative cell of origin of BHD-associated renal tumours (left panel) and sporadic ChRCCs in TCGA cohort (KICH) (right panel) predicted by COOBoost algorithm. Groups of gFOXI1, gNeutral and gL1CAM correspond to those in Fig. 2d and e. (b) The plots show the results of MutationTimeR algorithm. The dot plots show variant allele frequencies (VAF) of point mutations; purple dot indicates clonal mutation occurred at late stage, green dot indicates clonal mutation occurred at early stage, blue dot indicates clonal mutation occurred at unknown stage, red dot indicates subclonal mutation (left upper panels in each case). The stacked barplots show copy number of each allele; dark and light grey bars indicate major and minor allele, respectively (left middle panels in each case). The box plots with median values and 95% confidence intervals indicate predicted mutation timings of primary and secondary gains; blue bar indicates mono-allelic gains (N:1), pink bar indicates copy neutral (CN)-LOH/loss + gain (N:0) and green bar indicates bi-allelic gains (N:2) (left lower panels in each case). The histograms show magnified timelines of left lower panels in each case (right panels in each case).