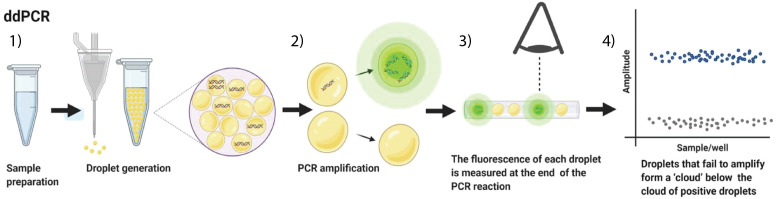
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of a digital droplet PCR workflow. From left to right: The DNA sample is prepared by generating water-in-oil droplets containing template and the necessary PCR reagents and dyes (1); The droplets are thermally cycled until the PCR reactions reach their end-point (2); The presence of an amplicon (and hence target DNA in the sample) in each droplet is visualized by dsDNA binding dye or by sequence-specific probes and is detected in a microfluidics device (3). Fluorescent signals are processed to detect and quantify the number of pathogens in the sample (4) (Adapted from Kokkoris et al., 2021).