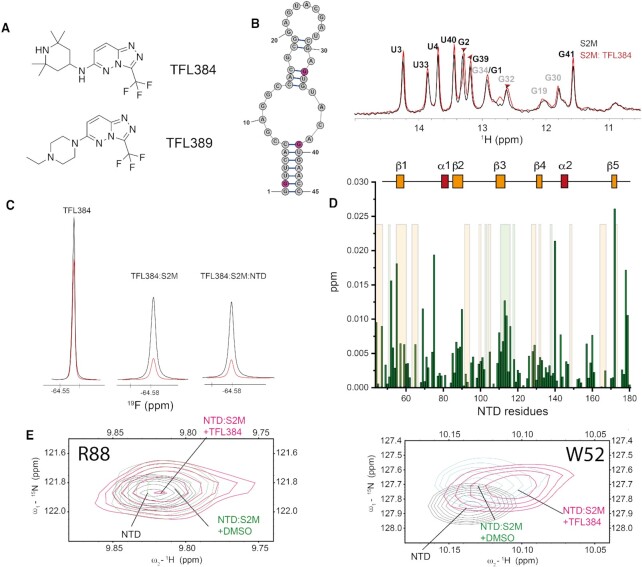
Figure 6.
(A) Structure of fragments TFL384 and TFL389. (B) Overlay of 1D 1H-SOFAST NMR focusing on the imino region highlighting the chemical shift perturbation induced by TFL384 (1.5 mM) on s2m-CoV-2 (50 μM, 25 mM Na Phos, 50 mM NaCl pH 6, 298 K). (C) 19F relaxation of TFL384 in the absence and presence of s2m-CoV-2 and NTD. Black: 1D 19F recorded using 5 ms relaxation delay; Red: 1D 19F recorded using 200 ms relaxation delay (50 mM Na Phos, 100 mM NaCl pH 6.8, 310 K). (D) Plot of combined 1H and 15N chemical shift perturbations induced by TFL384 (1.5 mM) to NTD amino acid residues of the NTD-s2m-CoV-2 complex (100 μM; orange shaded areas serve as a reference to residues perturbed s2m-CoV-2 to facilitate the comparison between the effect of RNA in presence or absence of TFL384). (E) 1H–15N HSQC overlay of selected regions underscoring the effect that TFL384 has at the RNA binding interface of NTD (50 mM Na Phos, 100 mM NaCl pH 6.8, 310 K).