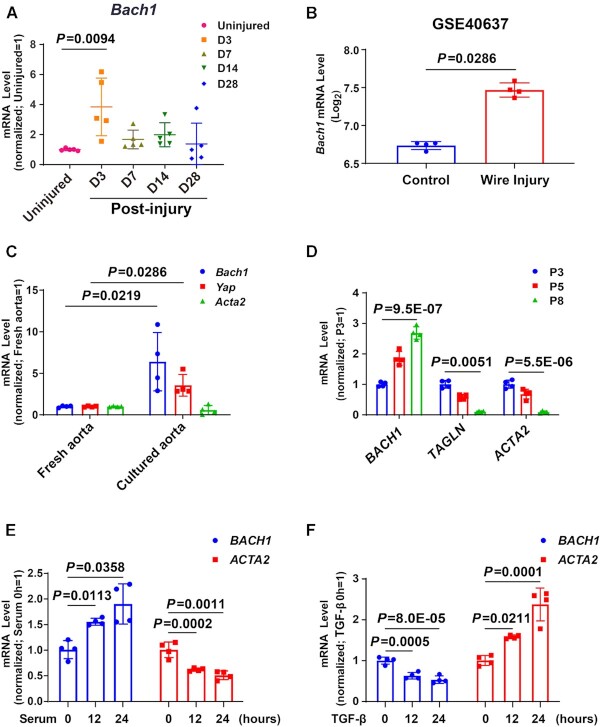
Figure 2.
The expression of BACH1 is increased during VSMC phenotype switching progress. (A) Bach1 was significantly upregulated three days after injury in the murine femoral artery wire injury model. Total RNA was collected from the uninjured (day [D] 0) and injured femoral arteries (D3, D7, D14, and D28 postinjury) and RT-qPCR analyses were conducted to obtain relative expression levels. (n = 5 each group, Plots showing mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post-hoc tests). (B) Bach1 mRNA expression was upregulated comparing wire injured femoral artery with uninjured femoral artery in the public microarrays from mouse femoral artery (GEO accession no. GSE40637) (n = 4 each group, data are mean ± SD showing log2 mean ± SD. unpaired two-tail t-test). (C) RT-qPCR was used to examine the mRNA (Bach1, Yap, Acta2) levels in the freshly isolated aortas and the aortas cultured in DMEM containing 20% serum for 3 days (n = 4 independent experiments, data are mean ± SD. unpaired two-tail t-test). (D) HASMCs with the indicated passage number (P3, P5 or P8) were subjected to RT-qPCR analysis to obtain relative expression levels of BACH1, TAGLN, and ACTA2 (n = 4 independent experiments, data are mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post-hoc tests). (E, F) HASMCs subjected to serum starvation for 24 hours were used as the control and then harvested after the indicated stimulations and time points: Serum stimulation at 12 or 24 h (E), or TGF-β stimulation at 12 or 24 h (F). Total RNA was extracted and subjected to RT-qPCR analysis to obtain relative expression levels of BACH1 and ACTA2 (n = 4 independent experiments, data are mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post-hoc tests).