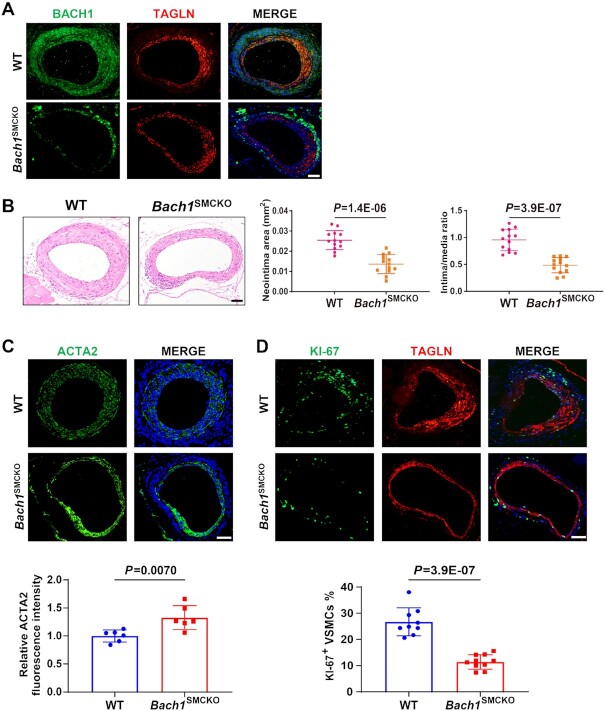
Figure 3.
VSMC-specific loss of Bach1 in mice attenuates the neointima formation after wire injury. (A) Bach1SMCKO mice exhibited specific loss of BACH1 expression in VSMCs of femoral artery following tamoxifen treatment by immunostaining (BACH1, green; TAGLN, red, and DAPI, blue). Scale bar: 100 μm. (B) Bach1SMCKO mice exhibited a significant decrease of injury-induced neointima formation compared with the wild-type (WT) mice, with representative HE staining images and quantification of neointima area, and intima-to-media ratio (n = 13 for each group, data are mean ± SD. unpaired two-tail t-test). Scale bar: 100 μm. (C) and (D) Bach1SMCKO mice exhibited a significant increase of ACTA2 expression (C) and a reduction of KI67-positive VSMCs (D) in the neointima at D28 after femoral artery wire injury compared with the wild-type mice, with representative images and quantification data (n = 6 for each group in (C); n = 10 for Bach1SMCKO mice and n = 9 for WT mice (D). Data are mean ± SD. unpaired two-tail t-test). Scale bar: 100 μm.