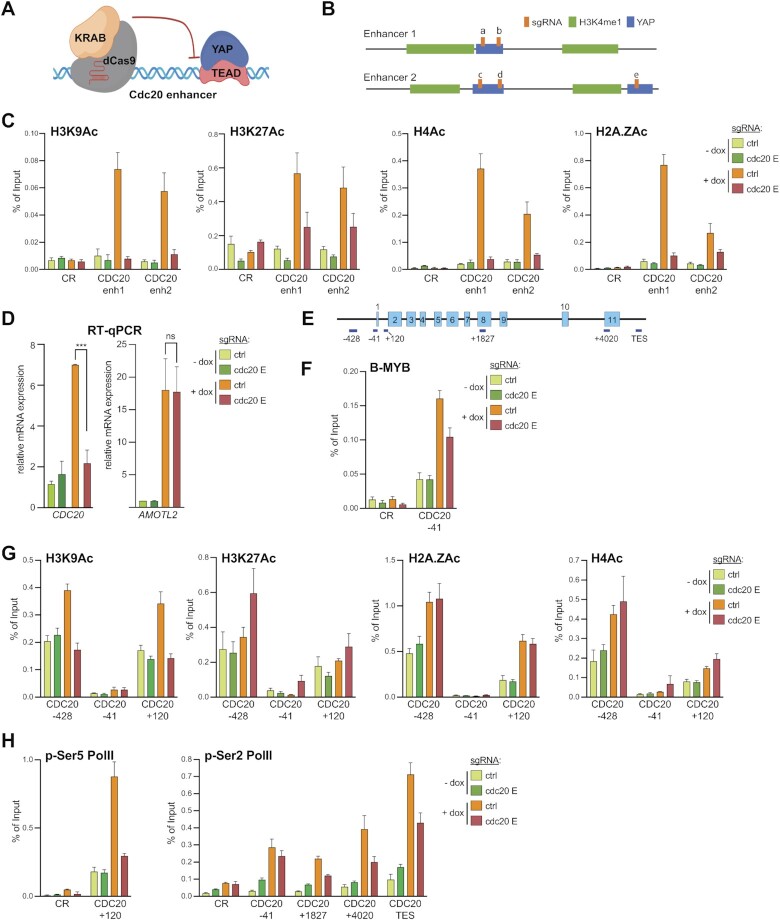
Figure 3.
A role for YAP-bound enhancers in histone acetylation and RNA Pol II Ser5 phosphorylation at the CDC20 locus. (A) Illustration of the CRISPR-interference (CRSPRi) system to inhibit YAP-bound enhancers. (B) Scheme depicting the two CDC20 enhancers (E1 and E2) and position of sgRNAs (A–E) in relation to the YAP (blue) and H3K4me1 (green) peaks as determined by ChIP-seq. (C) ChIP-qPCR for H3K9Ac, H3K27Ac, H4Ac and H2A.ZAc at the two CDC20 enhancers before and after YAP5SA induction in cells expressing either a control guide RNA or enhancer-specific guide RNAs demonstrating that targeted CRISPRi interferes with enhancer activation by YAP5SA. CR: negative control region. (D) MCF10A-YAP5SA-Cas9-KRAB cells expressing either control or enhancer-specific guide RNAs were treated with doxycycline (+dox) to induce the expression of YAP5SA and Cas9-KRAB or were left untreated (–dox). The expression of CDC20 and AMOTL2 relative to GAPDH was analyzed by RT-qPCR. Error bars: represent SD. N = 3 independent replicates. Student's t-test. ****P< 0.0001, ns = not significant. (E) Scheme of the CDC20 locus and the position of amplicons used for ChIP-qPCR. (F–H) ChIP-qPCRs at CDC20 indicated locus for (F) B-MYB, for (G) H3K9Ac, H3K27Ac, H4Ac and H2A.ZAc for (H) p-Ser5 Pol ll, p-Ser2 Pol ll and before and after YAP5SA induction in MCF10A-Cas9-KRAB cells expressing either a control guide RNA or enhancer-specific guide RNAs. CR: negative control region. For all ChIP-qPCR assays the mean and SDs of technical triplicates of a representative experiment (n = 2–3 biological replicates) are shown. Panel A was created with Biorender.com.