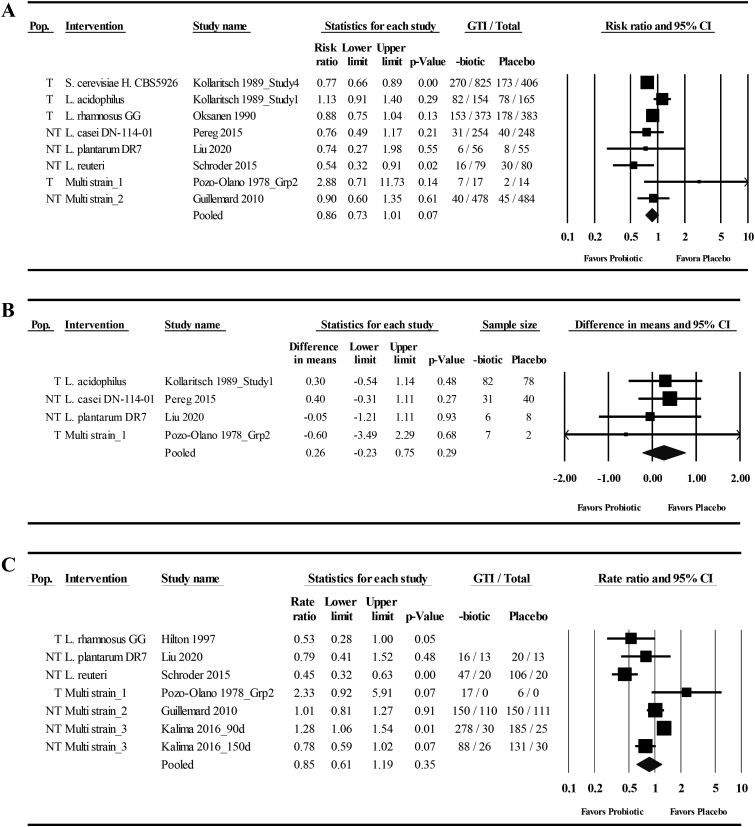
FIGURE 2.
Forest plots of the effects of orally ingested probiotics compared with placebo on the incidence and duration of gastrointestinal tract infections (GTIs) in nonelderly adults. (A) Risk of experiencing ≥1 GTIs (I2 = 51.8, P = 0.04); (B) days per individual GTI episode (I2 = 0, P = 0.86); (C) total days of illness with GTI (I2 = 84.1, P < 0.001). (A–C) Complete case random-effects meta-analysis using the inverse variance method by DerSimonian and Laird [60]. Individual study effect estimates (squares; sized by study weight) and pooled effects (diamonds) are plotted. Lower and upper limits are 95% CIs. Grp, group; H., Hansen; L., Lactobacillus; NT, nontraveler; Pop., population; S., Saccharomyces; T, travelers. Multistrain_1: L. acidophilus, L. bulgaricus; Multistrain_2: L. casei DN-114-001, Streptococcus thermophilus, L. delbreuckii; Multistrain_3: L. rhamnosus GG, B. animalis ssp. lactis BB12.