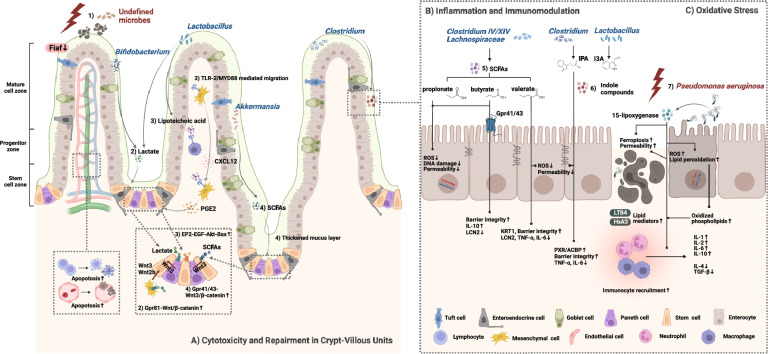
Fig. 2.
A Microbe-host interactions in radiation injury attenuation and augmentation. Microbes impact radiation injury development by regulating cytotoxicity and repairment in crypt-villous units: 1 Undefined microbes suppress the secretion of Fiaf from epithelium, thereby aggravating enteritis by increasing apoptosis of lymphocytes and endothelial cells in villus mesenchyme. 2 Probiotics-derived lactate interacts with Gpr81 on Paneth cells and stromal cells to stimulate secretion of Wnt3 and Wnt2b, which prompt epithelial replenishment by activating β-catenin pathway in intestinal stem cells. 3 Lactobacillus-derived lipoteichoic acid activates TLR-2/MYD88 on macrophages to induce secretion of chemotactic CXCL12 which binds CXCR4 to mediate the migration of mesenchymal stem cells to where intestinal stem cells locate, so as to boost enterocyte regeneration through the PGE2-EP2-EGF-Akt-Bax pathway. 4 Akkermansia-derived acetate and propionate bind Gpr41/43 to up-regulate the Wnt3/β-catenin-RAS-ERK pathway in intestinal stem cells, so as to promote their renewal and differentiation into secretory cells demonstrated as the thickened mucus layer. B SCFAs and indole compounds produced by representative microorganisms impose radio-protection through regulating inflammation and immune reseponse: 5 SCFAs promote anti-inflammation response and decrease barrier permeability by decreasing DNA damage and cell loss as well as by increasing expression of proteins related with gut integrity maintainment. 6 IPA reactivates the post-radiation declined PXR/ACBP pathway to control inflammation and improve gut integrity. C Microbiota-regulated oxidative stress augments radiation injury: Psedumonas aeruginosa-derived 15-lipoxygenase increases lipid peroxidation, induces ferroptosis and exacerbates inflammation by promoting immunocyte recruitment and elevating proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines and lipid mediators. Pro-inflammatory molecules: LCN2, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1, IL-2, LTB4, HxA3; anti-inflammatory markers: IL-10, IL-4, TGF-β. Fiaf fasting-induced adipose factor, Gpr G-protein-coupled receptor; TLR-2 Toll-like-receptor-2, PGE2 prostaglandin E2, EP2 E prostaglandin recepter-2, EGF epidermal growth factor, SCFA short chain fatty acid, IPA indole-3-propionic acid, I3A indole-3-carboxaldehyde, ROS = reactive oxygen species, LCN2 lipocalin, KRT1 Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 1, PXR pregnane X receptor, ACBP acyl-CoA binding protein, LTB4 leukotriene B4, HxA3 hepoxilin A3. Created with Biorender.com