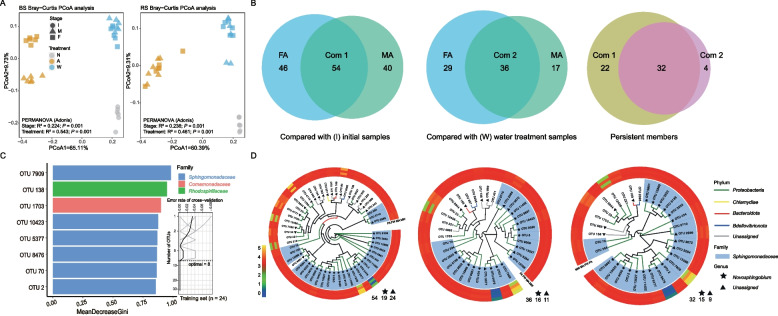
Fig. 2.
Variations in rhizobacterial communities under exogenous glycyrrhizin addition. a Principal coordinate analysis of rhizobacterial communities between two sampling compartments (BS, bulk soil; RS, rhizosphere soil) among different sampling stages and treatments. b Venn diagrams of enriched and persistent taxa between different treatments. I, initial sampling stage; M, middle sampling stage; F, final sampling stage; A, allelochemical treatment; W, water treatment. N, no treatment in initial samples. c The top eight bacterial families were identified using random-forest classification of the relative abundance of the persistent rhizobacterial taxa in allelochemical and water treatments. Bioindicators are ranked in descending order of importance to the accuracy of the model. The inset represents tenfold cross-validation error as a function of the number of input families used to differentiate allelochemical and water treatment rhizobacteria in order of variable importance. d Phylogenetic trees and relative abundance heatmaps of corresponding enriched and persistent taxa