Figure 2.
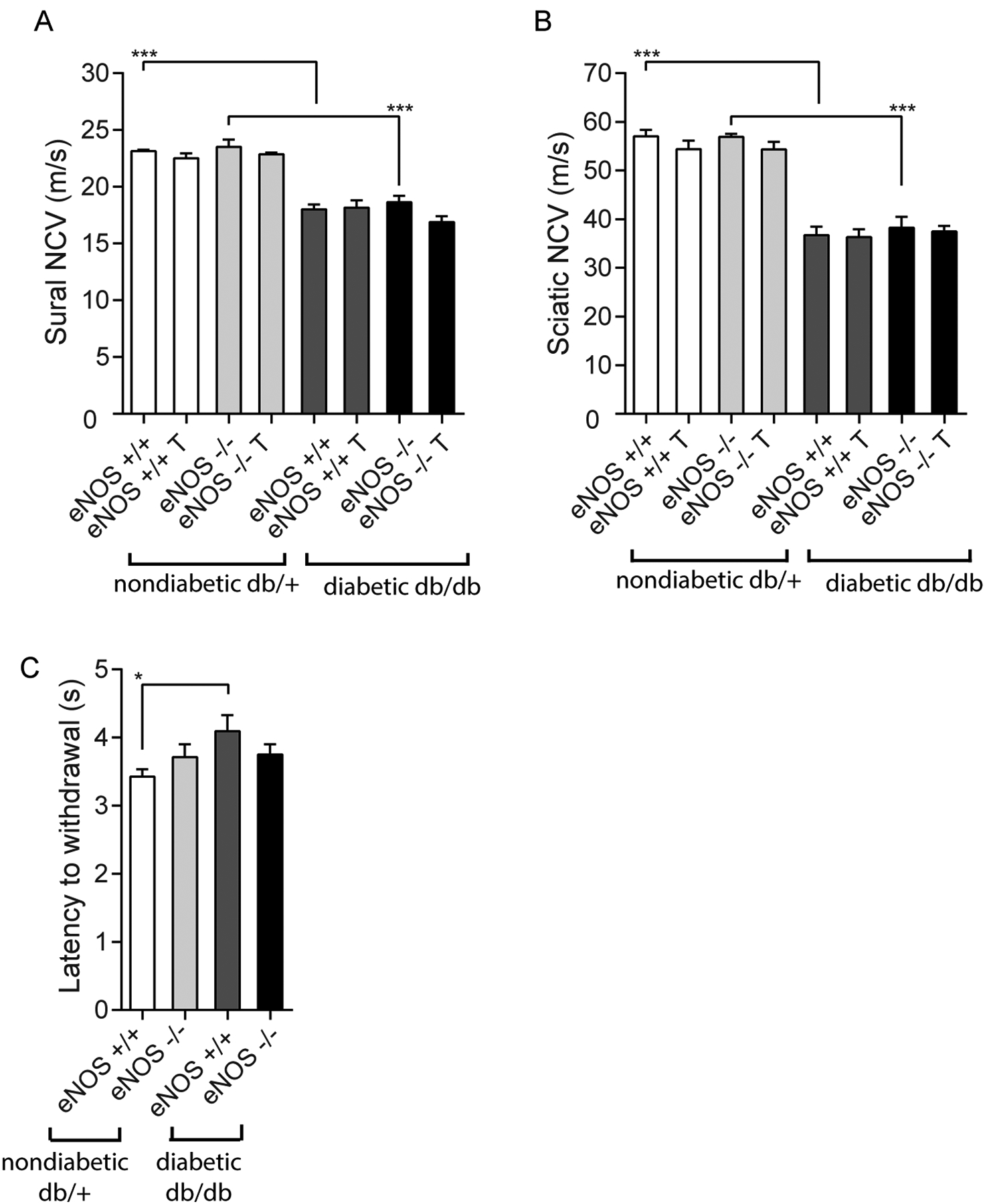
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) phenotype for the 8 experimental groups to demonstrate the effects of diabetes and eNOS deletion. Sural (Panel A) and sciatic (Panel B) nerve conduction velocities (NCVs) decreased in db/db animals, but were not influenced by either eNOS deletion or RAS inhibitor treatment. Similarly, latency to withdrawal of hind paw (Panel C) was modestly increased in diabetes but was not clearly affected by eNOS deletion *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001. T, indicates RAS inhibitor treatment.
