FIG. 1.
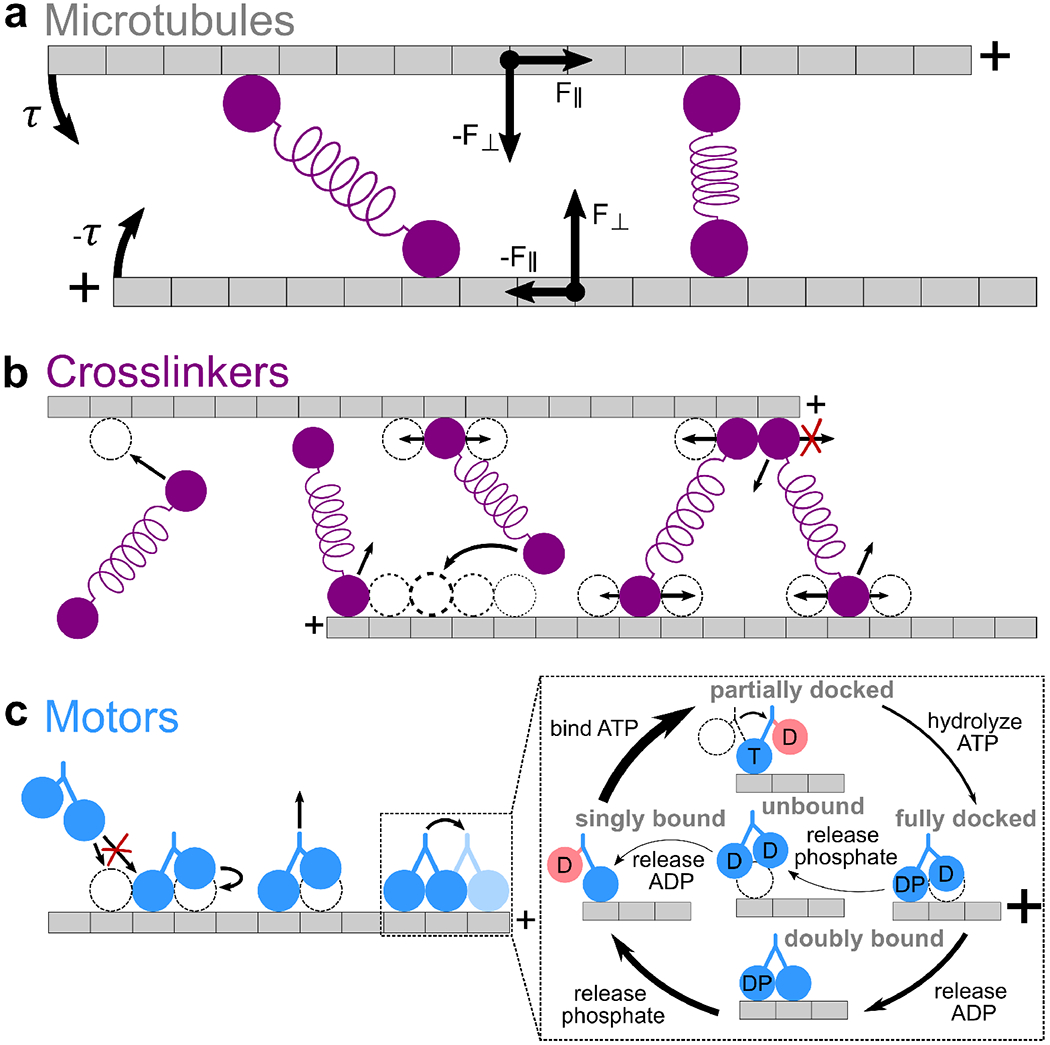
CyLaKS model ingredients A. Microtubules. Microtubules are modeled as single protofilaments, where each tubulin dimer corresponds to a discrete site on a 1-D lattice. Each microtubule has a plus-and minus-end. Associated proteins exert force and torque on filaments, causing 2-D translaton and rotation about each filament’s center of mass. B. Crosslinkers. Each crosslinker head can independently bind to, unbind from, and diffuse on the filament lattice. The relative probability of the second head binding to each sites is represented by dotted circles of different thickness. The relative probability of heads diffusing is represented by arrow length. Steric exclusion prevents more than one crosslinker head from occupying the same binding site. Crosslinker heads cannot diffuse off filament ends. C. Motor proteins. Motors can bind to, unbind from, and step toward the plus-ends of filaments. Inset, mechanochemical cycle. Motor heads can be bound to ADP (D), ATP (T), ADP·Pi (DP), or nothing (empty). Red coloring labels head which cannot bind to the microtubule due to necklinker tension. Arrow thickness represents the relative probability of each transition. Steric exclusion prevents more than one motor head from occupying the same binding site.
