FIG. 3.
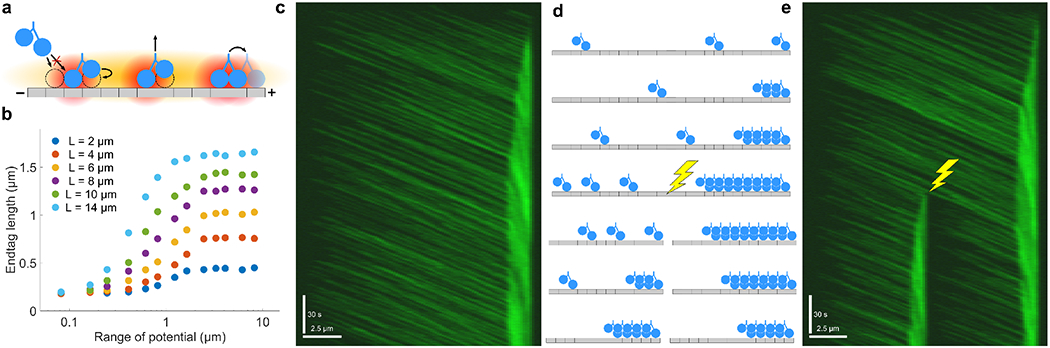
Kif4A end-tag formation due to long-range motor interactions A. Schematic of the motor interaction model. Motors interact by short-and long-range cooperativity, and the long-range interaction affects both binding and stepping. B. Plot of end-tag length versus potential range for varying microtubule length. C. Simulated kymograph of end-tag formation. 67% of simulated motors are fluorescently labeled. Scale bars are 2.5 μm and 30 seconds. D. Schematic of the microtubule ablation simulation. After an end-tag forms, the microtubule is split in half. A new end-tag forms on the new microtubule, while the old end-tag shrinks. E. Simulated kymograph of microtubule ablation simulation. 67% of simulated motors are fluorescently labeled. Scale bars are 2.5 μm and 30 seconds.
