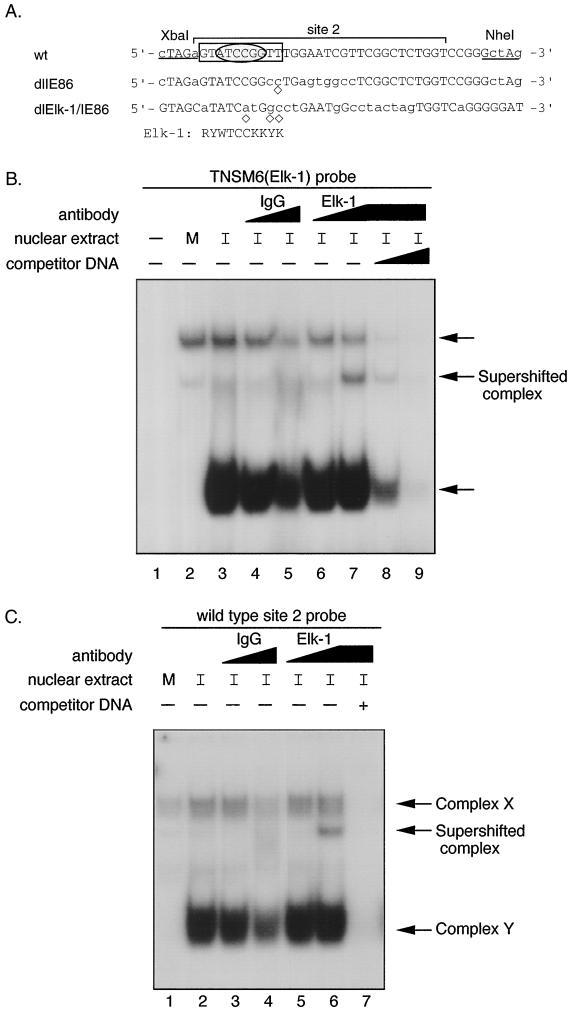
FIG. 8.
Transcription factor Elk-1 in DNA-protein complex Y. (A) Comparison of the DNA sequence of dlIE86 and dlElk-1/IE86 with wild-type (wt) site 2 DNA. Site 2 (−169 to −139) is designated by a bracket. The mutated nucleotides are shown in lowercase letters. The computer-predicted Elk-1 consensus binding site is shown and also boxed in the wt probe. Abbreviations: R = A or G; Y = C or T; W = A or T; K = G or T. ◊, nucleotide which does not fit the Elk-1 consensus sequence. The sequence in an oval reflects the core consensus for Elk-1/SAP-1 binding. (B) EMSA and competition assay with TNSM6 (Elk-1) probe. Nuclear extract from either mock-infected or HCMV-infected (24 hpi) HFFs was incubated with or without 10- or 50-fold molar excess of nonradioactive wild-type site 2 DNA at RT for 15 min before either control IgG or anti-Elk-1 IgG antibody was added. The IgGs were at the same protein concentrations. The reaction mixture was incubated at RT for 30 min, and then probe was added. The complexes were fractionated as described in Materials and Methods. Lanes: 1, TNSM6 probe alone; 2, TNSM6 probe plus mock-infected HFF nuclear extract; 3, TNSM6 probe plus HCMV-infected HFF nuclear extract; 4 and 5, same as lane 3, plus 1 μl (lane 4) or 5 μl (lane 5) of control IgG; 6 and 7, same as lane 3, plus 1 μl (lane 6) or 5 μl (lane 7) of anti-Elk-1 (IgG) polyclonal antibody; 8 and 9, same as 7, plus a 10- or 50-fold molar excess of nonradioactive wild-type site 2 DNA, respectively. M, mock infection; I, 24 h HCMV infection. (C) EMSA and competition with wild-type probe and IgG or anti-Elk-1 (IgG) polyclonal antibody as described for panel B, except lane 7 contains a 50-fold molar excess of nonradioactive wild-type site 2 DNA. Complexes X and Y are indicated by arrows.