Fig. 1.
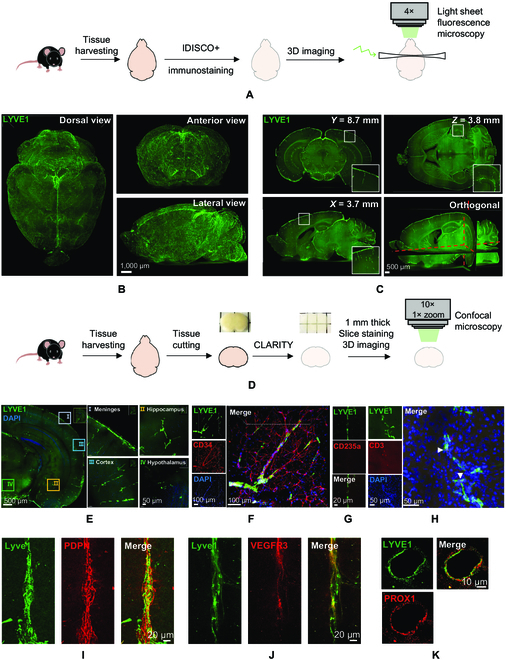
Lymphatic vessels exist deep in the mouse brain. (A) Schematic representation of experimental design of iDISCO+ tissue clearing procedure, immunostaining, and whole-brain imaging by light-sheet microscopy. (B) Light-sheet microscope fluorescent images of LYVE1 immunostaining of cleared whole-mount brain from different views. (C) Examples of optical sections taken from of whole-mount mouse brain from coronal (Y), sagittal (X), horizontal (Z), and orthogonal planes. Insets: Selected areas within the optical sections magnified to show the fluorescent signal of LYVE1 staining. (D) Schematic representation of experimental design of CLARITY tissue clearing procedure, immunostaining, and confocal microscopy imaging of thick brain sections. (E) Confocal images of LYVE1 fluorescent in cleared 1-mm-thick coronal brain section from mouse brain. Selected areas within the section magnified to show the fluorescent signal of LYVE1 staining in different areas. (F) Coimmunostaining of LYVE1 and CD34 in 1-mm coronal section. (G) Coimmunostaining of LYVE1 and CD235a in 16-μm brain section. (H) Same as (F) but coimmunostaining of LYVE1 and CD3. White arrows indicate T cells detected within the deep brain lymphatic vessels. (I) Coimmunostaining of LYVE1 and podoplanin (PDPN) in 16-μm brain section. (J) Same as (I) but coimmunostaining of LYVE1 and VEGFR3. (K) Same as (I) but coimmunostaining of LYVE1 and PROX1. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.
