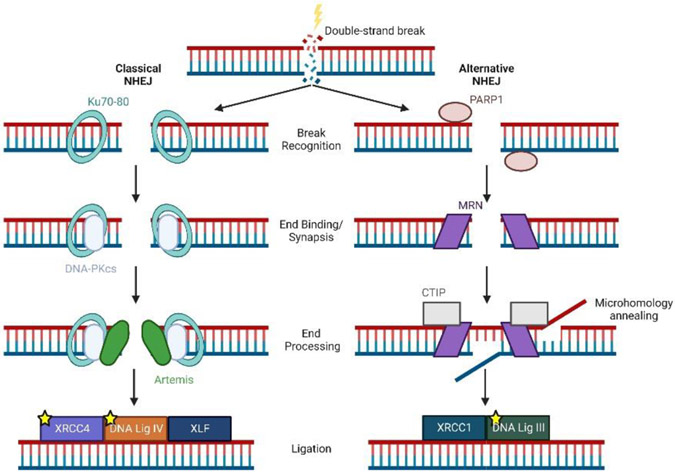
Figure 3. Classical and alternative nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) pathways.
After the formation of a double-strand break, the classical (left) or the alternative (right) nonhomologous end-joining pathways repair DNA damage through break recognition, end binding/synapsis, end processing, and final ligation of DNA. Proteins marked with a yellow star have been shown to have decreased expression during aging.