Fig. 2. Identification of hCONDELs with species-specific activity perturb TF-binding motifs.
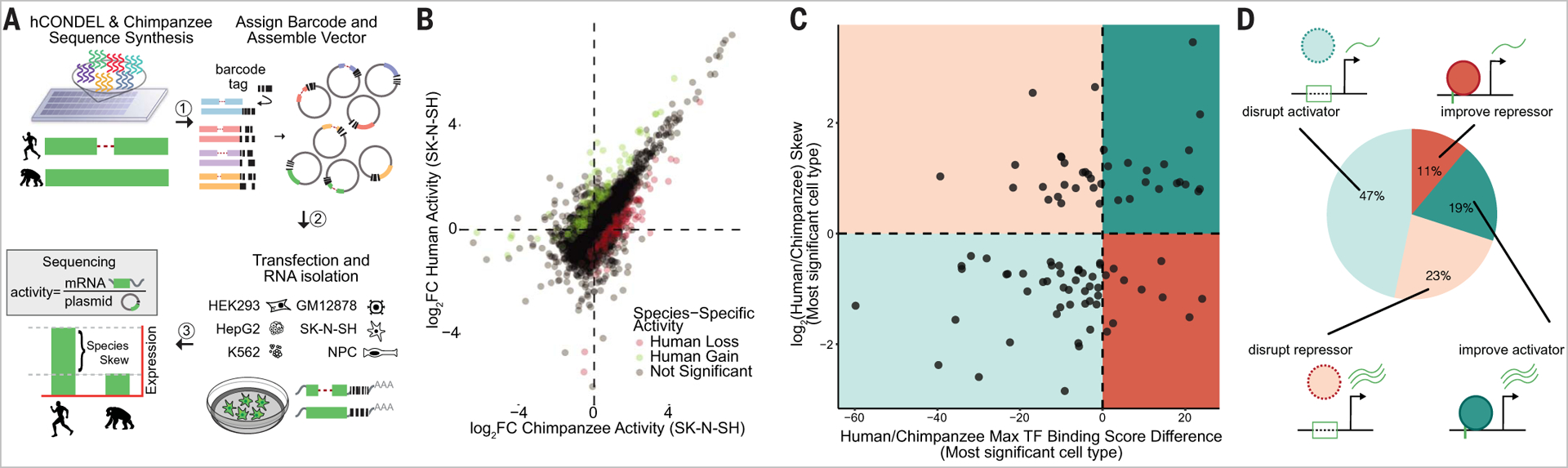
(A) MPRA characterization strategy. (B) Identification of hCONDELs with significant (BH adjusted P < 0.05) species-specific activity. Regulatory activity for chimpanzee sequence x axis versus orthologous human sequence (y axis) showing significant human loss (red) and gain (green). Illustrative SK-N-SH data are plotted. (C) Species activity correlated with predicted TF alteration score [difference in log-likelihood (base 2) in human versus chimpanzee sequence motif match]. Data from the cell type with the most significant MPRA-measured effect are shown. (D) Breakdown of regulatory activity and TF-binding differences categorized into activators (teal) and repressors (red), with either improved (solid line) or diminished (dashed line) motif prediction.
