FIG. 2.
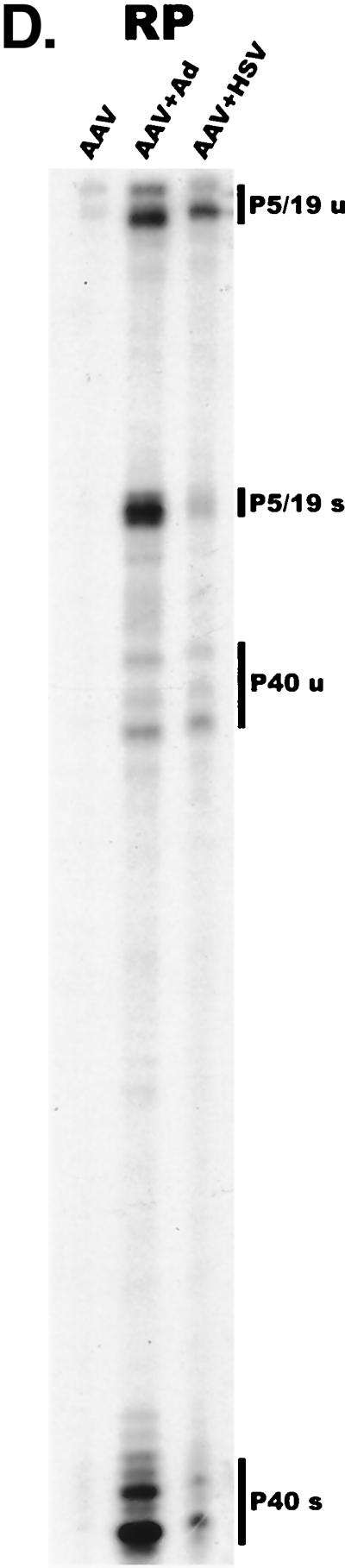
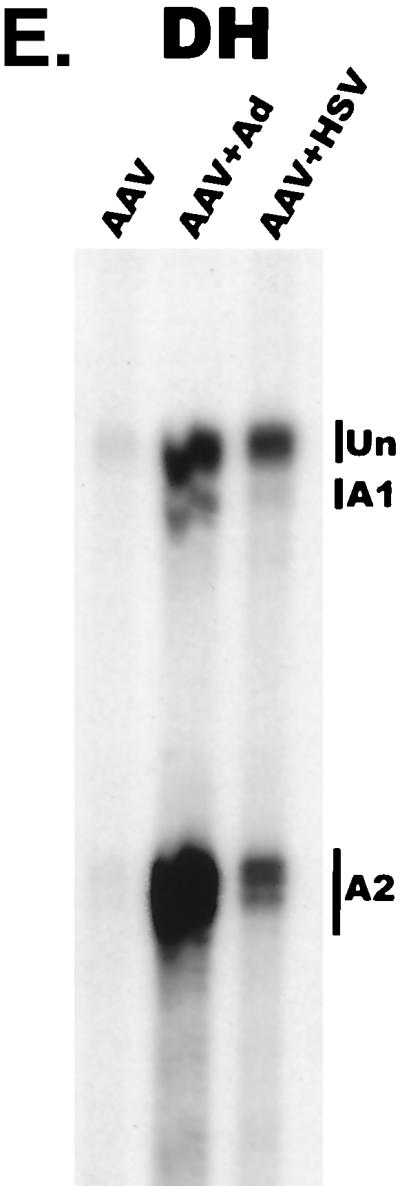
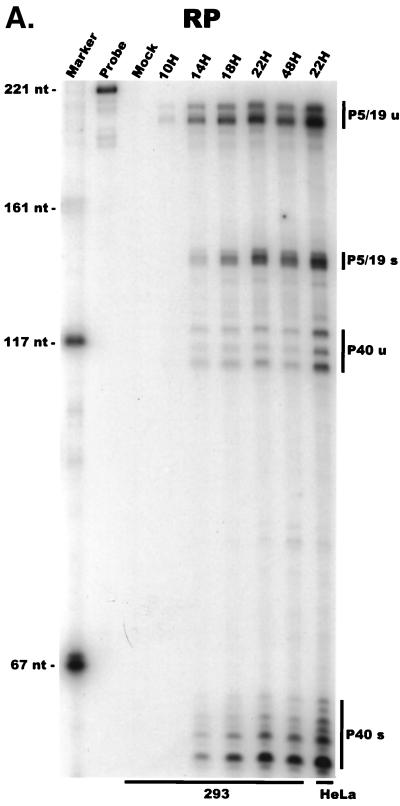
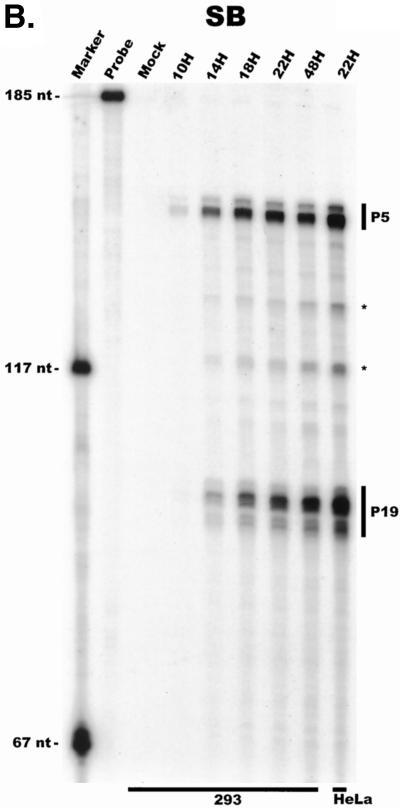
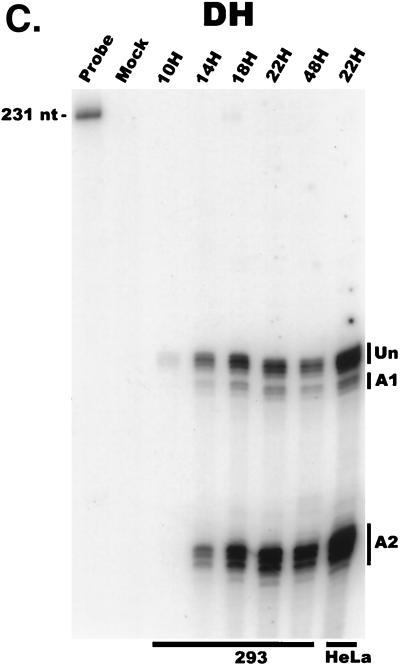
AAV RNA accumulates in a temporal manner during helper virus coinfection. (A) P5/19 unspliced transcripts are detectable prior to significant accumulation of other AAV RNAs. The RP probe was used to protect 10 μg of total RNA isolated at indicated times from infected 293 or HeLa cells (indicated at the bottom). Cells were coinfected with AAV (MOI = 10) and Ad (MOI = 2 to 5) at time zero. AAV-specific products are indicated on the right (u, unspliced; s, spliced). Marker and Probe lanes display reference size standards which are indicated on the left. Lanes labeled Mock display protections of uninfected 293 cell RNA. Multiple bands seen for the probes spanning P19 and P40 likely reflect the use of multiple initiation sites within these regions; additional bands may include incomplete RNase digestion of probe-RNA complexes. (B) P5-generated transcripts are detectable before significant accumulation of those generated by P19. The SB probe was used to protect the same RNA and exactly as described for panel A. At 10 h postcoinfection, P5 transcripts predominate. Later in infection (18 to 221 h), P19 products accumulate to approximately two- to threefold-greater levels than P5 products. Asterisks indicate likely breakdown products of P5 protected fragments and were excluded from quantification. (C) Levels of spliced versus unspliced RNAs increase over the course of infection. The DH probe was used to protect the same RNA samples as above exactly as described for panel A, except that the nt 161 marker had just run off the bottom of this gel. (D) Coinfection of AAV with HSV yields AAV steady-state RNA ratios similar to those found after AAV-Ad coinfection. The RP probe was used to protect 10 μg of total RNA isolated from 293 cells approximately 24 h after infection with AAV (MOI = 10) alone, coinfection with Ad (MOI = 2 to 10), or coinfection with HSV (MOI = 2 to 10). In this experiment, likely due to infection conditions, the level of AAV expression in response to HSV coinfection was atypically low. The ratio of the various RNA species, however, remains the same. (E) HSV stimulates AAV splice acceptor usage similarly to Ad. The DH probe was used to protect the same RNA samples as used for the experiments shown in panel D.