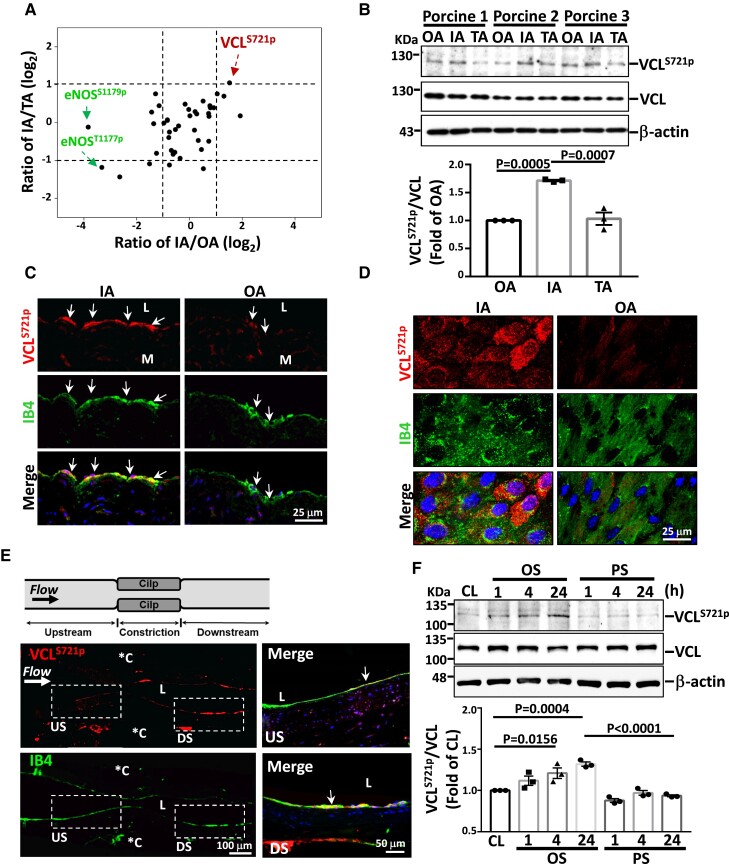
Figure 1.
VCLS721p is highly expressed in ECs exposed to disturbed flow in vivo and in vitro. (A) Approximately 107 cells were freshly scraped from the precisely defined areas of IA, OA, and TA of six pigs and subjected to large-scale phosphoproteomics analysis (n = 3). Results show the relative ratios of critical phosphoproteins in the IA compared with OA and TA. (B–D) Western blot analysis of VCLS721p expression in fresh porcine aortic ECs (B, n = 3), immunohistochemical staining of the cross-sections of the porcine aortic arch (C), and en-face immunostaining of the ApoE−/− mouse aortic arch (D). (E) Longitudinally panoramic examination of EC VCLS721p expression from the upstream (US) through the midpoint to the downstream (DS) areas of the constriction in the experimentally stenosed rat abdominal aorta. *C indicates clip-injured areas. Right panels show the magnified views of the indicated areas (white dashed line box). (F) ECs were kept under static condition as controls (CL) or subjected to oscillatory (OS) or pulsatile (PS) shear stress for the indicated times (n = 3). Arrows in C and E indicate the EC layer stained with an antibody against isolectin B4 (IB4). Data in B and F are means ± SEM and were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparison test. The pictured images represent three independent experiments with similar results.