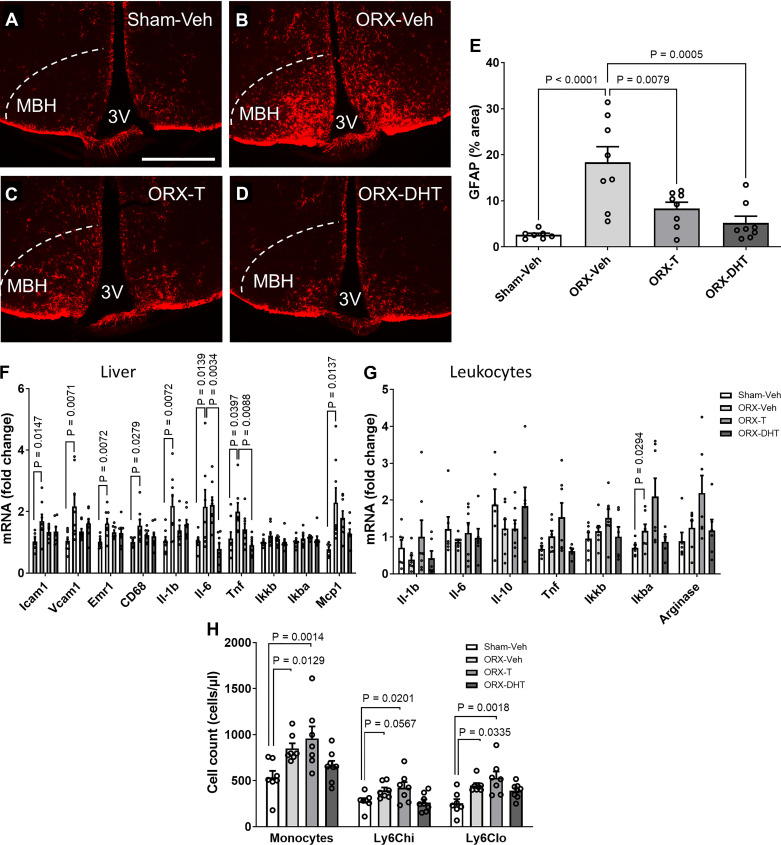
Figure 4.
Chronic central infusion of testosterone (T) and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) reduces hypothalamic astrogliosis and peripheral risk markers in orchiectomized (ORX) mice exposed to high-fat, high-sucrose diet (HFHS). A–D: representative images showing glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) immunoreactivity in the mediobasal hypothalamus (MBH) of sham operated (Sham)-vehicle (Veh) (A), ORX-Veh (B), ORX-T (C), and ORX-DHT (D). 3V, third ventricle. Scale bar, 500 µm. All mice were injected with AAV-D377Y-mPCSK9 and fed with HFHS and received intracerebroventricular infusion for 28 days. E: quantification of GFAP-positive area percentage in the MBH from 6 sections per animal. F and G: mRNA levels of inflammatory markers in liver (F) and circulating leukocytes (G). H: quantification of total monocyte and monocyte subset cell numbers determined by flow cytometry. In E and H, data are presented as means ± SE of 8 mice per group. In F and G, data are presented as fold change relative to Sham-Veh.