FIGURE 5.
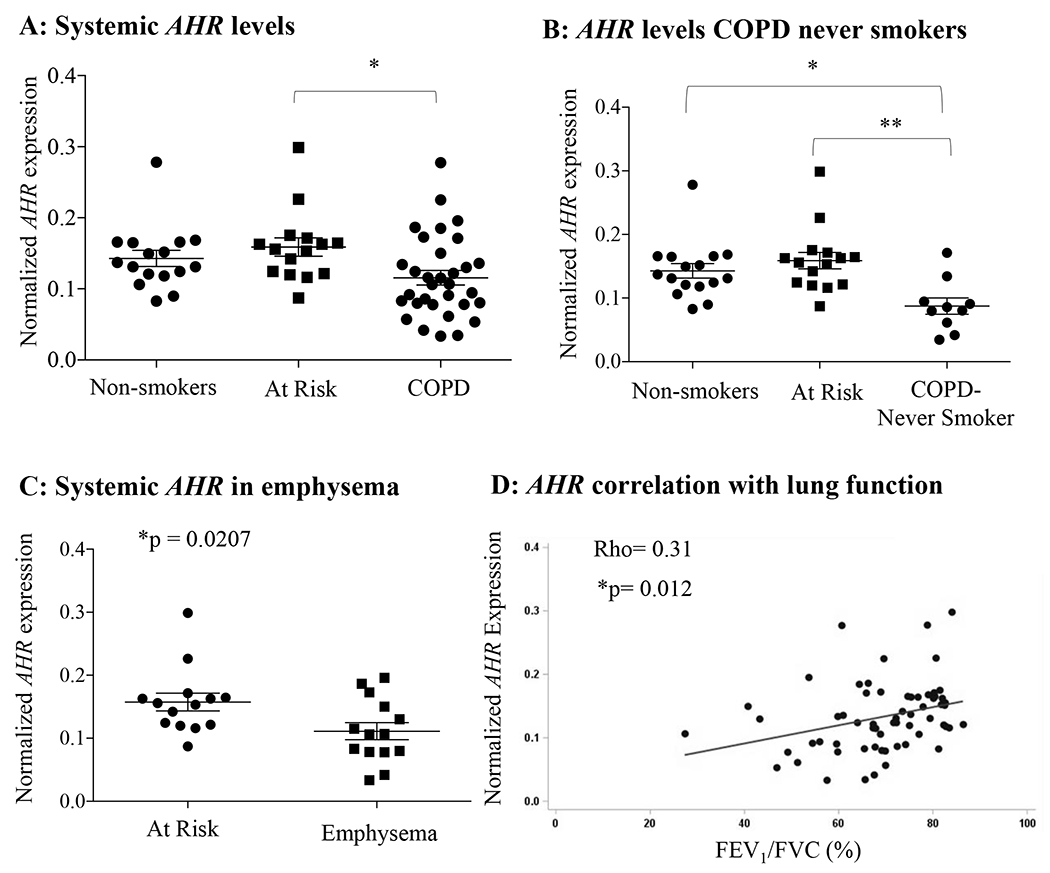
AHR expression is significantly reduced in the blood of human COPD subjects from the CanCOLD cohort. A: There was significantly less systemic AHR mRNA in COPD subjects relative to the “At Risk” subjects (*p< 0.05). B: AHR mRNA expression was significantly less in COPD subjects with no history of smoking (COPD-Never smokers) relative to both Non-smokers and At Risk control subjects (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). Results are expressed as mean ± SEM. C: AHR mRNA expression was significantly less in COPD subjects that had also been diagnosed with emphysema via CT (Emphysema) relative to At Risk control subjects. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM. D: There was a significant positive correlation between systemic AHR mRNA expression and lung function (FEV1/FVC) as assessed using a Pearson’s correlation coefficient.
