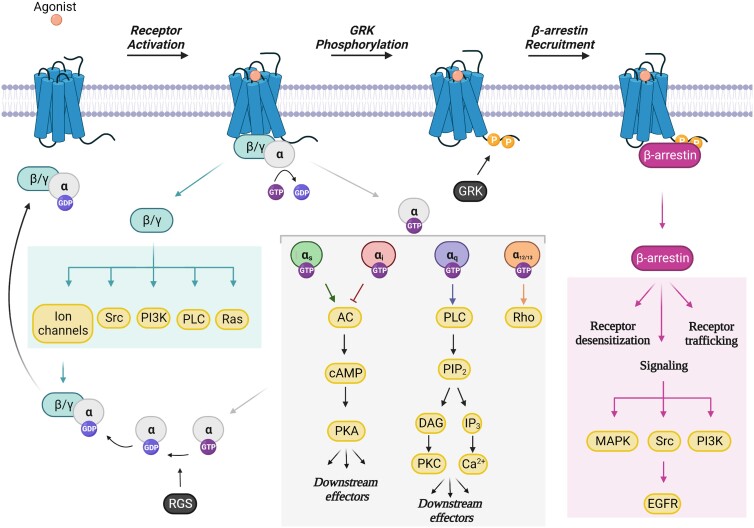
Figure 1.
GPCR activation and downstream signalling. Following agonist binding, GPCRs recruit heterotrimeric G proteins (Gα, β, γ) and induce the exchange of GDP for GTP on Gα. The Gα and Gβγ subunits subsequently dissociate forming two activated G protein units that independently transduce signals to downstream effectors. The four families of Gα (Gαs, Gαi, Gαq, and Gα12/13) activate distinct signalling cascades, thereby generating unique cellular responses. RGS proteins accelerate the GTPase activity of Gα, thereby leading to the inactivation of G protein signalling. GRK-mediated phosphorylation of the COOH-terminus of the receptor facilitates the recruitment of β-arrestin, which in turn, promotes receptor desensitization, receptor trafficking/recycling, and β-arrestin-dependent signalling mechanisms. GDP, guanosine diphosphate; GTP, guanosine triphosphate; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PLC, phospholipase C; AC, adenylyl cyclase; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; PKA, protein kinase A; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; DAG, diacylglycerol; PKC, protein kinase C; IP3, inositol trisphosphate; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; GRK, GPCR kinase; RGS, regulators of G protein signalling. Figure generated with Biorender.com.