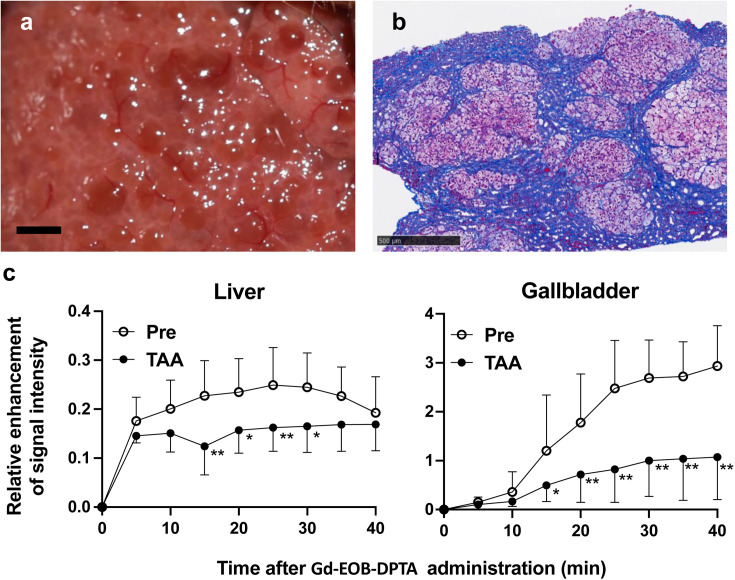
Fig. 1.
Hepatic fibrosis induced by thioacetamide (TAA) in marmosets. a. Nodular liver surface of a marmoset subcutaneously injected with TAA at a dose of 30 mg/kg twice a week for 15 months. Scale bar (black): 2 mm. b. Liver biopsy specimen with Masson’s trichrome stain of a marmoset given the same treatment as in a. Fibrous lesions containing blue-stained collagen were largely located around hepatic lobules. Scale bar (black): 500 µm. c. Relative enhancement (RE) of signal intensity by dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI using gadolinium ethoxybenzyl diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid (Gd-EOB-DTPA), a hepatocyte-targeted contrast agent, before and 15 months post continuous TAA treatment. RE in the liver and gallbladder at time points after Gd-EOB-DTPA injection was significantly decreased post TAA treatment in marmosets (n=3). Statistical analysis was conducted by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test following two-way ANOVA. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.