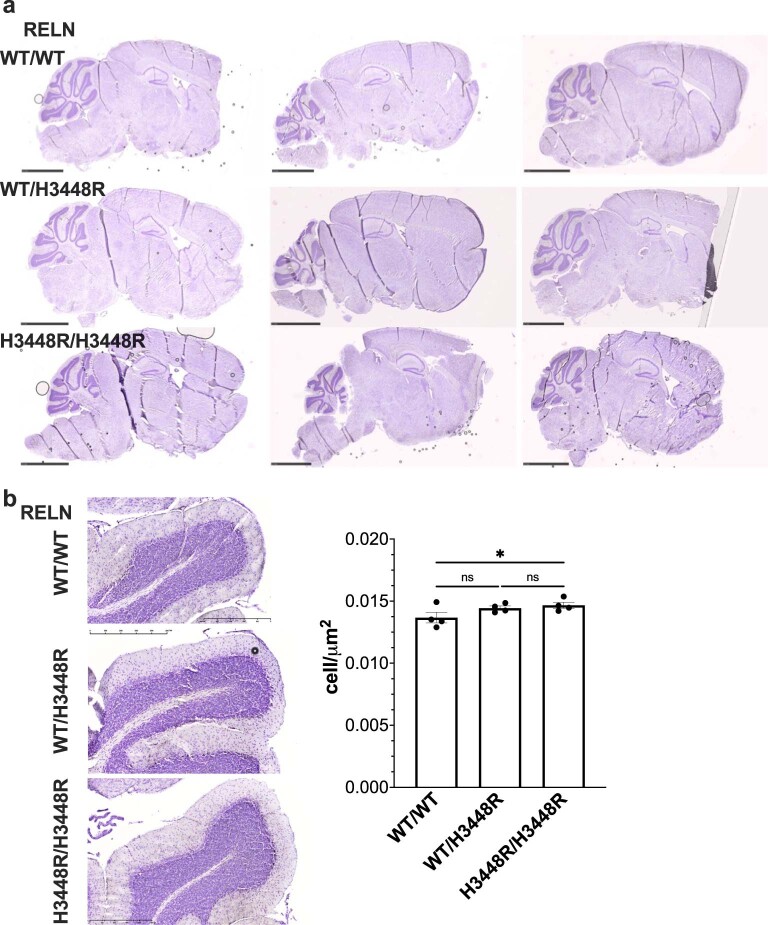
Extended Data Fig. 4. Increased neuronal density in the cerebellum’s granular layer in the presence of the H3448R RELN mice. presence of the H3448R RELN mice.
a, Representative Cresyl violet staining of n = 3 midsagittal sections from male RELN mice (WT/WT, WT/H3448R, H3448R/H3448R; 5–6-month-old mice). Data is showing that the H3448R variant does not affect qualitatively the gross anatomy, nor neuronal distribution in the whole brain. Scale bar, 2.5 mm. b, Cresyl violet staining of the granular region of the cerebellum, indicating an increased neuronal density in the homozygotes (H3448R/H3448R) as compared to wild type (WT/WT) and heterozygote (WT/H3448R) mice. Scale bar, 500 μm. c, Neuron density analysis of the granular layer of the RELN-H3448R cerebellum in comparisons to wild type. Data indicates a significantly increased neuron counting (*p = 0.0470, n1 = n2 = 4, t = 2.300, DF = 9) in homozygotes (H3448R/H3448R) as compared with wild type (WT/WT). One-way ANOVA, followed by Fisher’s LSD test post-hoc analysis for multiple comparison of n = 4 specimens for each genotype. Data is presented as mean ± S.D. At least 2 sections and 5 fields per section were analyzed for each specimen.