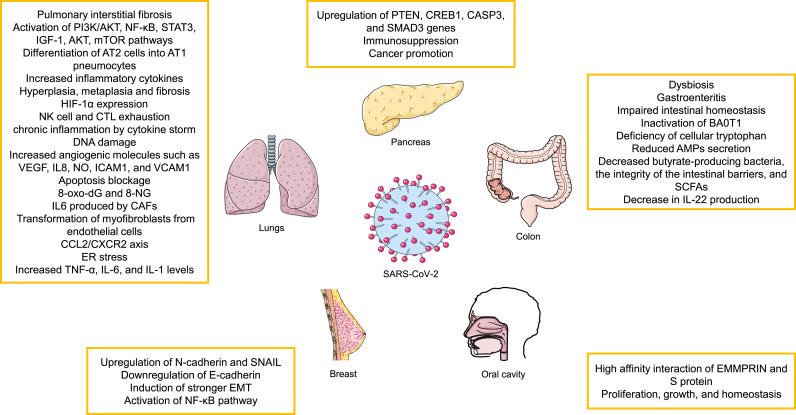
Fig. 2.
Possible oncogenic effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection on different organs. See text for more details. PI3K-AKT, Phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase and Protein Kinase B; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; AT, angiotensin; HIF-1α, Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha; NK, natural killer cell; CTL, Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte; VEGFA, Vascular endothelial growth factor A; IL, Interleukin; NO, nitric oxide; ICAM-1, Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; 8-oxo-Dg, 8-Oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine; 8-NG, 8-nitroguanine; CAF, cancer associated fibroblasts; CCL2/CXCR2, C–C Motif Chemokine Ligand 2/CXC chemokine receptor 2; ER, Endoplasmic reticulum; TNF, Tumor necrosis factor; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; CREB1, cAMP-regulatory element-binding protein-1; CASP3, caspase 3; SMAD3, SMAD family member 3; SNAIL, Zinc finger protein SNAI1; EMT, epithelial–mesenchymal transition; SCFA, Short-chain fatty acids; EMMPRIN, extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer.