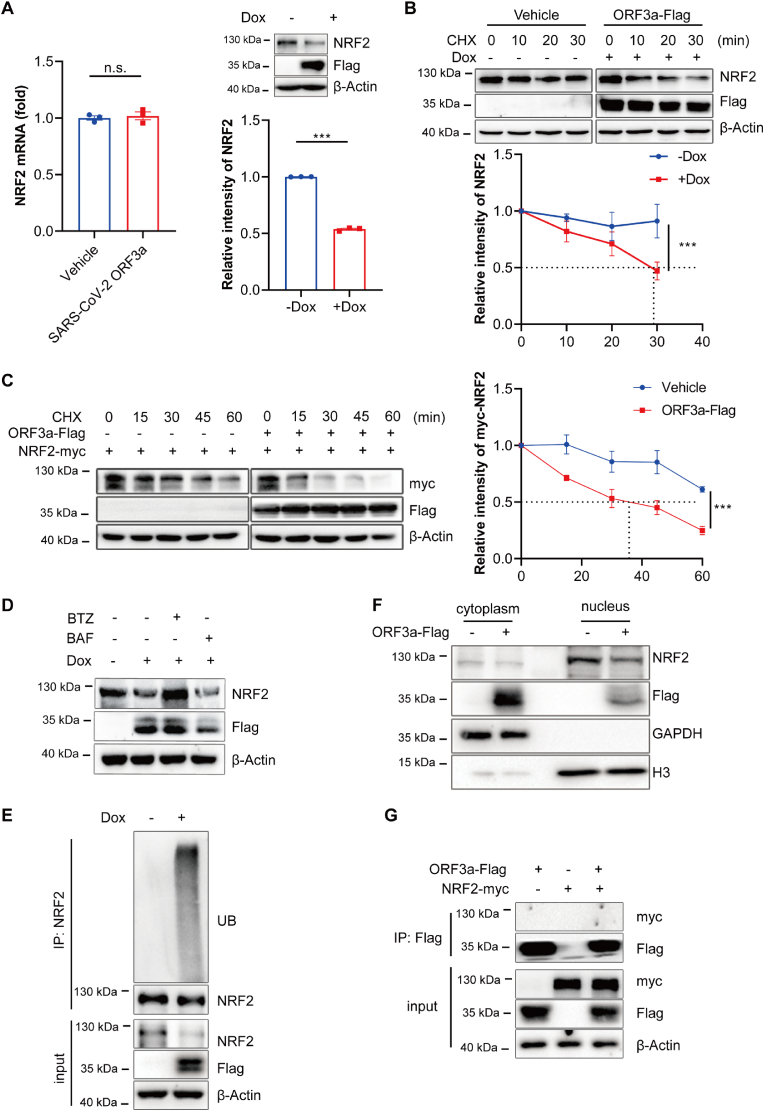
Fig. 5.
SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a promotes the degradation of NRF2. (A) Tet-on inducible NCI–H1299 cells were treated with or without doxycycline for 24 h, mRNA expression levels and protein levels of NRF2 were assayed. The relative intensities of NRF2 were quantified by ImageJ software. Data show mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. (B) Tet-on inducible NCI–H1299 cells were treated with doxycycline followed by treatment with cycloheximide (CHX) for the indicated time courses. Lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting. The relative intensities of NRF2 were quantified by ImageJ software and and mean ± SEM from three independent replicates were shown. (C) HEK 293T cells were transfected with NRF2-myc alone or with ORF3a-Flag for 24h followed by CHX treatment for the indicated time courses. Lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting. The relative intensities of NRF2-myc were quantified by ImageJ software and mean ± SEM from three independent replicates were shown. (D) Tet-on inducible NCI–H1299 cells were treated with or without doxycycline for 24 h, followed by treated with 1 μM BTZ or 200 nM BAF for 8 h and lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting. (E) Indicated NCI–H1299 cells were treated with 1uM BTZ for 8h and subjected to an in vivo ubiquitination assay. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-NRF2 antibody and analyzed with indicated antibodies. (F) Subcellular fractionation analysis was performed, followed by the immunoblotting analysis of cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions. (G) HEK 293T cells were transfected with ORF3a-Flag and NRF2-Myc for 36 h. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag beads and the precipitated proteins were detected with indicated antibodies. ***p ≤ 0.001, n.s. = not significant.