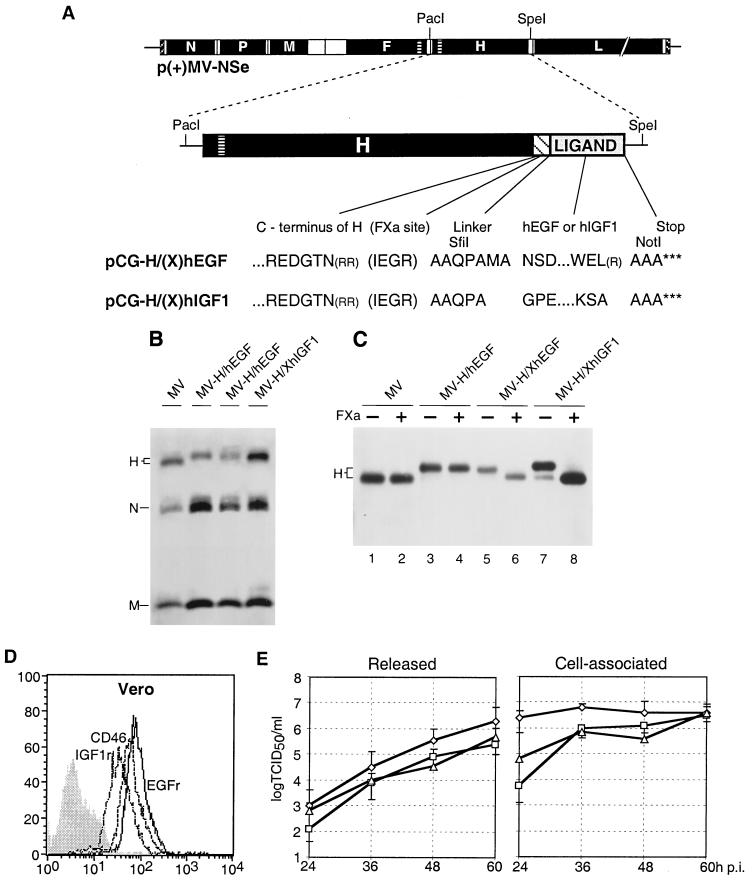
FIG. 1.
Genomic structure, protein composition, and replication of recombinant MV. (A) Plasmid p(+)MV-NSe coding for the MV antigenome (top), PacI-SpeI fragments used for subcloning (center), and amino acid sequences (one-letter code) of the junctions between the H protein ectodomain and the specificity domains (bottom). Coding regions of the six MV cistrons are represented by solid black boxes, the transmembrane segment of the F and H proteins by a horizontally lined box, the FXa cleavage site and the flexible linker by a hatched box, and the ligand by a gray box. Arginine residues in parentheses have been deleted. For details see text. (B) Protein composition of recombinant viruses. Viral particles were purified by centrifugation through a 20% sucrose layer onto a 60% sucrose cushion and subsequent pelleting. The viruses were titrated, 5,000 PFU was subjected to lysis, and proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE. For immunodetection, a MV-specific antiserum was used. (C) FXa protease sensitivity of hybrid H proteins. Purified viral particles (5,000 PFU) were lysed and incubated for 1 h without (−) or with (+) FXa protease at room temperature. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and detected with an H-specific antiserum. (D) FACS analysis of CD46 (interrupted line), IGF1r (dotted line), and EGFr (continuous line) expression on Vero cells. Vertical axis, cell number; horizontal axis, fluorescence intensity. The greyed profile represents incubation of the cells without the primary antibody. (E) Time course of released (left panel) and cell-associated (right panel) virus production in Vero cells infected with parental MV (diamonds), MV-H/XhEGF (squares), and MV-H/XhIGF1 (triangles). Cells were infected at a MOI of 3 and were incubated at 32°C for the times indicated. Viral titers were determined by 50% end-point dilution. Indicated values are averages of three experiments.