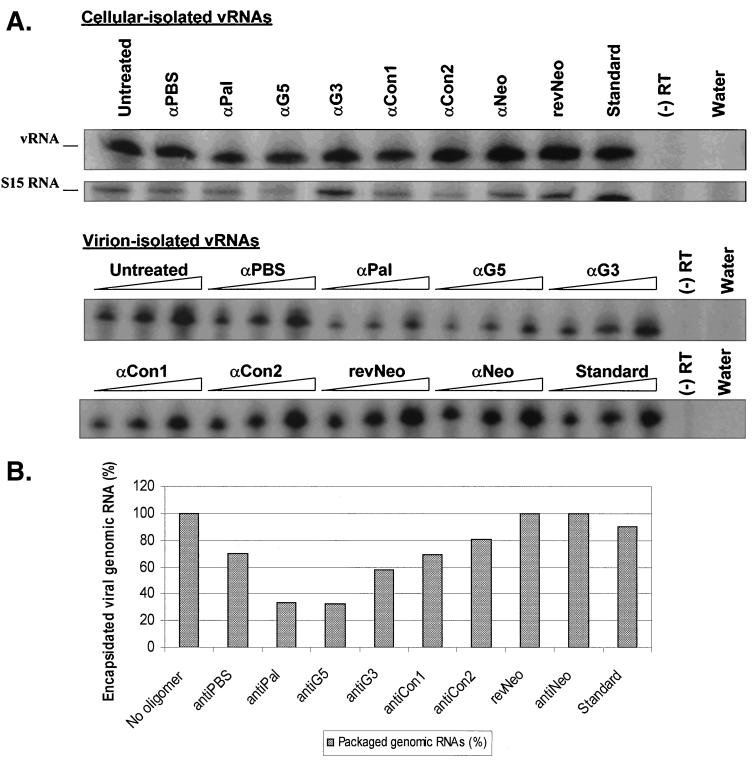
FIG. 6.
Reduction of viral genomic RNA encapsidation due to antisense DNA oligomers. (A) RT-PCR amplification of viral genomic RNAs. Polyclonal cells expressing the wild-type DLS sequence were treated either with one of a series of antisense DNA oligomers or with a medium control. RNAs were isolated from cells or virions. Various volumes of virion-isolated RNAs (5, 10, and 20 μl [indicated by the height of the triangle over each set of three lanes]) and 1.0 μg of cell-isolated RNAs were RT-PCR amplified. vRNA and S15 are PCR products amplified from viral RNA and control ribosomal protein S15 message, respectively. α, anti; (−) RT, one-step RT-PCR mixture lacking MuLV RT; Water, one-step RT-PCR mixture lacking the RNA substrate. (B) Relative reduction of genomic RNA packaging. Percentage reductions in genomic RNA encapsidation of the oligomer-treated samples relative to that of the untreated mixture were compared.