Figure 2.
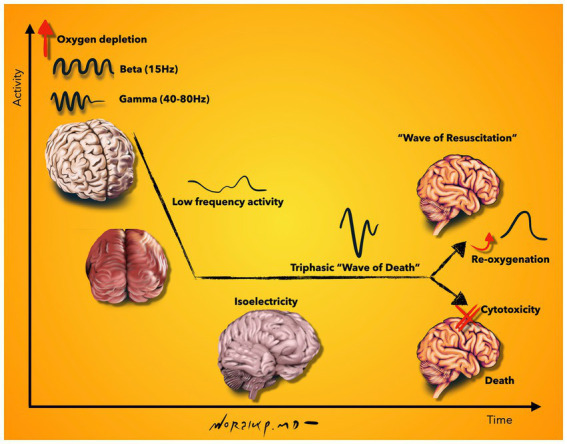
Schematic representation of neurophysiological activity during the final moments of life. Beta and gamma oscillations are increased shortly after oxygen depletion, which is followed by low frequency activity and isoelectricity. During isoelectricity, cortical neurons deploy membrane potential depolarizations, which are reflected on the EEG as a high-amplitude, sharply contoured triphasic wave, called the “wave of death.” Although all neurophysiological measurements are in line with a dead brain at this stage, a gradual repolarization can be initiated upon re-oxygenation of the brain; seen on EEG as the “wave of resuscitation.” If no re-oxygenation is supplied, loss of cell properties continue and result in cytotoxicity and death. Illustration based on findings described in Schramm et al. (2020). Illustration by Woralux Phusoongnern.
