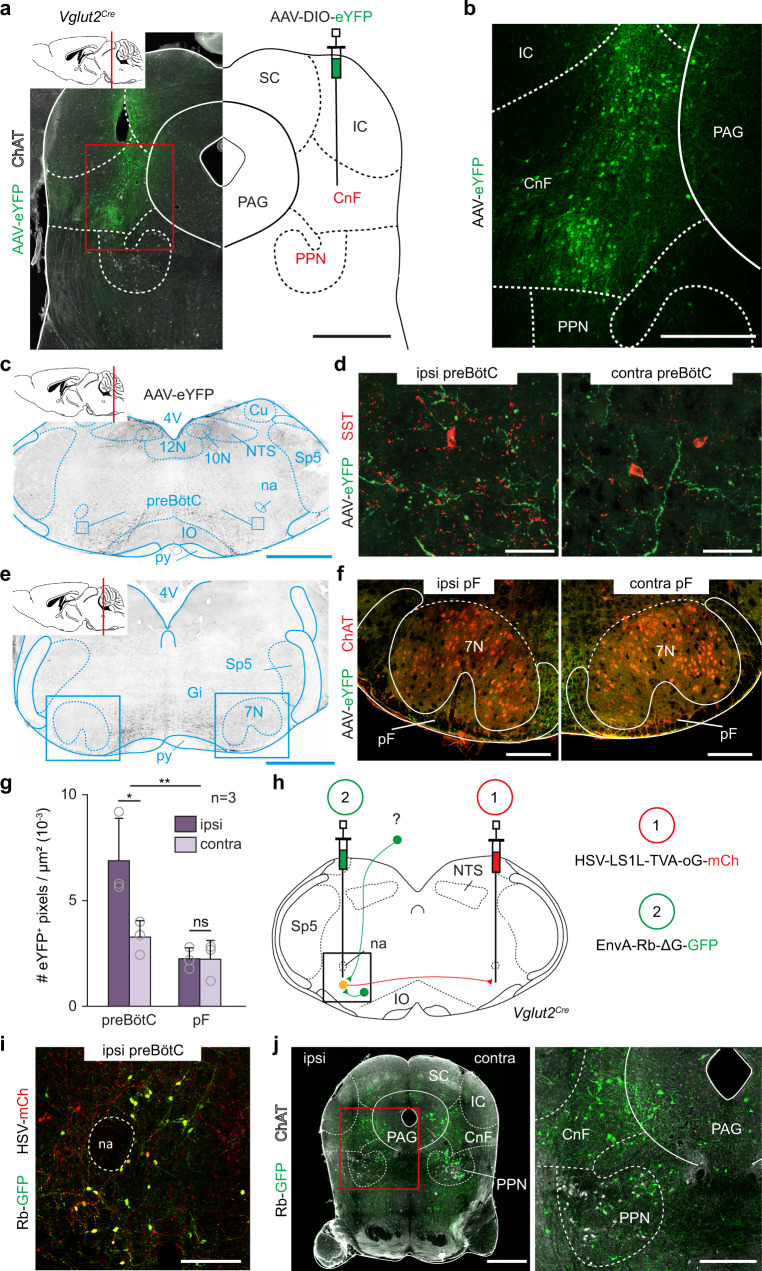
Fig. 1. CnF glutamatergic neurons contact the preBötC inspiratory generator.
a Strategy for tracing glutamatergic (Glut+) CnF projections. Cholinergic Pedunculopontine (PPN) neurons are identified by Choline Acetyl Transferase (ChAT) expression. Scale bar, 1 mm. b Magnification showing transfected cells in the Cuneiform Nucleus (CnF). Scale bar, 400 µm. c Transverse section showing CnF projections in the ventral reticular formation including the preBötC. Scale bar, 1 mm. d Magnifications over ipsilateral and contralateral preBötC containing somatostatin-expressing (SST+) cells. Note that the CnF projects to both sides with an ipsilateral predominance. Scale bar, 40 µm. e Transverse section showing the distribution of CnF projections at the level of the pF area. Scale bar, 1 mm. f Magnifications over ipsilateral and contralateral pF areas delineated around ChAT+ facial motoneurons (7N). Note very little CnF projections. Scale bar, 250 µm. a–f are representative of n = 3 animals. g Mean density ± SD of eYFP+ pixels in the preBötC and the pF areas. Gray circles are mean values of n individual mice. **p = 0.001; *p = 0.011; ns, p = 0.9102 (Wilcoxon matched-pairs tests; preBötC and pF: 9 sections per side). Source data are provided as a Source data file. h Strategy for retrograde transsynaptic monosynaptic tracing from Glut+ commissural preBötC neurons. EnvA-ΔG-Rb-GFP: G-deleted and EnvA pseudotyped rabies virus. i Magnification showing double-transfected “starter” cells in the preBötC. Scale bar, 200 µm. j Left: transverse section showing putative presynaptic cells in the CnF and PPN. Scale bar, 1 mm (left), 250 µm (right). i, j are representative of n = 3 animals (3 males). See also Figs. S1 and S2. Abbreviations used in all figures: PAG periaqueductal gray, IC inferior colliculus, SC superior colliculus, PPN pedunculopontine nucleus, CnF cuneiform nucleus, 4V fourth ventricle, 10N dorsal motor nucleus of vagus, 12N hypoglossal motor nucleus, NTS nucleus tractus solitarius, py pyramidal tract, IO inferior olive, Cu cuneate nucleus, na nucleus ambiguus, preBötC pre-Bötzinger complex, pF parafacial respiratory area, Sp5 spinal trigeminal nucleus, 7 N facial nucleus, Gi gigantocellular reticular nucleus.