Fig. 8. Graphical representation of revealed circuits.
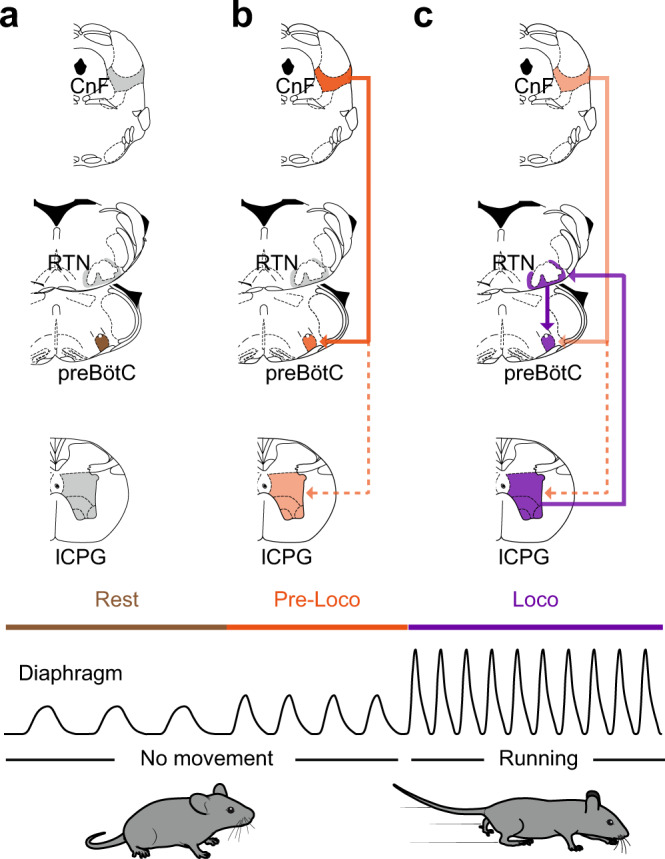
a At rest, and in the absence of locomotor initiation signal from the CnF to the locomotor central pattern generator (lCPG), the preBötC drives the basal inspiratory rate. b CnF activation leads to an augmented ventilation before the animal engages in effective running. This “pre-loco” phase is attributed to the CnF sending a direct and rapid activation signal to the preBötC (thick line). In contrast, the CnF signal crosses multiple synapses before reaching the locomotor CPG16,65 (dashed line), which may support a longer latency to locomotor onset. c CnF activation eventually leads to a running episode, during which ventilation is augmented further. This effect is attributed to the activated lCPG sending direct projections to the pF respiratory area, and in particular to the RTNPhox2b/Atoh1 neurons, which in turns contact and activate the preBötC (thick lines).
