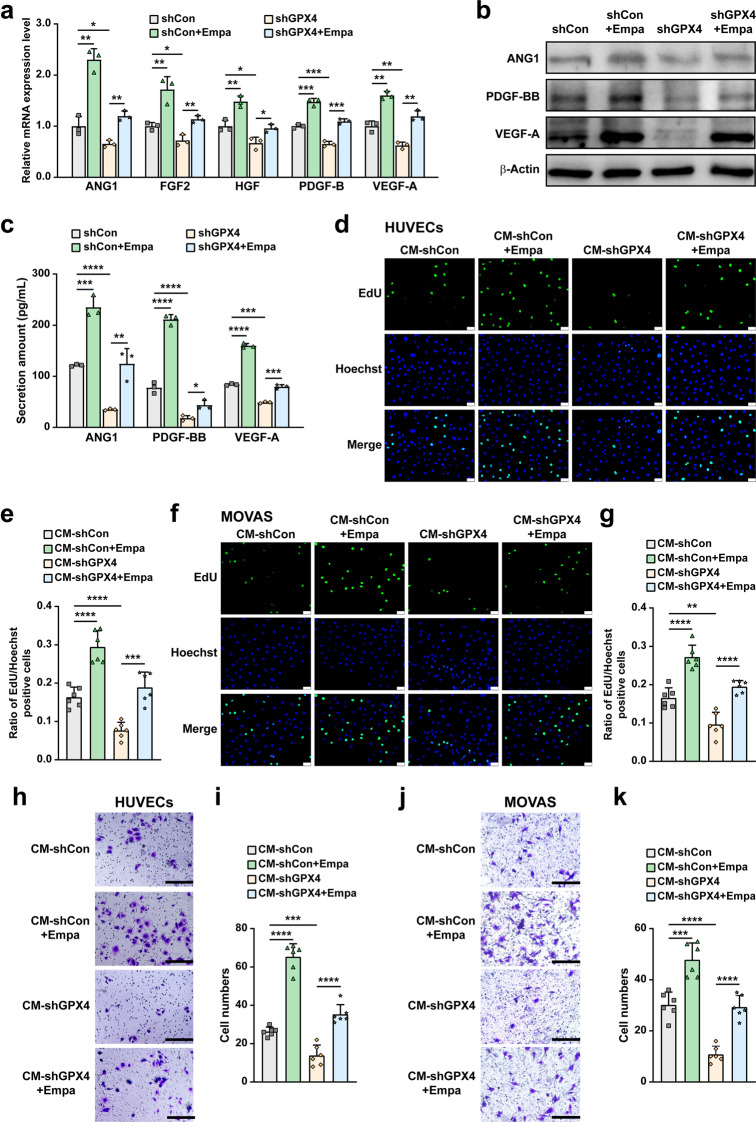
Fig. 6. Empagliflozin promotes blood vessel-forming cells proliferation and migration by enhancing skeletal muscle cells paracrine function in a GPX4-dependent manner.
mRNA (a) and protein (b) expression of angiogenic factors in GPX4-knocked down C2C12 cells treated with 10 μM empagliflozin, as examined using qRT-PCR and Western blotting, respectively. β‐Actin was used for qRT-PCR normalization and as Western blotting loading control. c Secreted amount of ANG1, PDGF-BB and VEGF-A in the culture medium of C2C12 cells treated with 10 μM empagliflozin, as analyzed using ELISA. Proliferation potential of HUVECs (d, e) and MOVAS cells (f, g) cultured with indicated conditioned media collected from GPX4-knocked down C2C12 cells treated with 10 μM empagliflozin, as examined using EdU incorporation assay. Representative images (d and f; scale bars: 100 μm) and quantification results (e and g; n = 6) were shown. Migration potential of HUVECs (h, i) and MOVAS cells ( j, k) cultured with indicated conditioned media, as analyzed using transwell migration assay. Representative images (h and j; scale bars: 200 μm) and quantification results (i and k; n = 6) were shown. All experiments were performed under hyperglycemia. Data were presented as mean ± SD (n = 3, unless further indicated). CM-shCon and CM-shGPX4: conditioned media obtained from shCon-transfected or GPX4-knocked down C2C12 cells; CM-shCon+Empa and CM-shGPX4+Empa: conditioned media obtained from shCon- or shGPX4-transfected C2C12 cells treated with 10 μM empagliflozin. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.