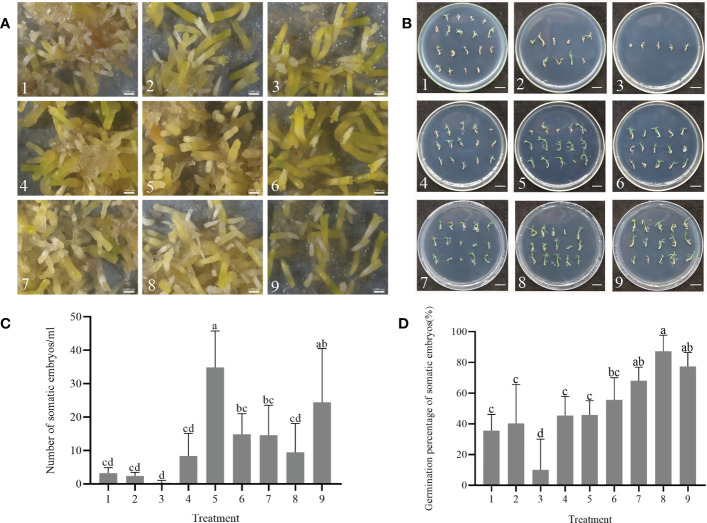
Figure 2.
Effect of combined treatments with abscisic acid (ABA), polyethylene glycol 8000 (PEG 8000), activated carbon (AC), and maltose on somatic embryo maturation and germination of P. massoniana. (A) The callus surface was different degrees of yellow, brown or green color after 75 days. The somatic embryos were visible at different maturation medium compositions under the stereomicroscope. Scale bar = 0.1 cm. (B) Somatic embryos germinated for one month. Scale bar = 1.0 cm. (C) Number of somatic embryos in different treatments after 75 days of maturation. (D) Germination rate of somatic embryos. Data represent mean ± SD of replicates. Different lowercase letters above the bars indicate a significant difference using ANOVA and Duncan’s test (p < 0.05). Numbers represent maturation medium composition supplemented with 1: 1 mg/L ABA, 110 g/L PEG 8000, 0.5 g/L AC and 20 g/L maltose. 2: 1 mg/L ABA, 130 g/L PEG 8000, 1.0 g/L AC and 25 g/L maltose. 3: 1 mg/L ABA, 150 g/L PEG 8000, 1.5 g/L AC and 30 g/L maltose. 4: 2 mg/L ABA, 110 g/L PEG 8000, 0.5 g/L AC and 30 g/L maltose. 5: 2 mg/L ABA, 130 g/L PEG 8000, 1.0 g/L AC and 20 g/L maltose. 6: 2 mg/L ABA, 150 g/L PEG 8000, 1.5 g/L AC and 25 g/L maltose. 7: 3 mg/L ABA, 110 g/L PEG 8000, 0.5 g/L AC and 25 g/L maltose. 8: 3 mg/L ABA, 130 g/L PEG 8000, 1.0 g/L AC and 30 g/L maltose. 9: 3 mg/L ABA, 150 g/L PEG 8000, 1.5 g/L AC and 20 g/L maltose.