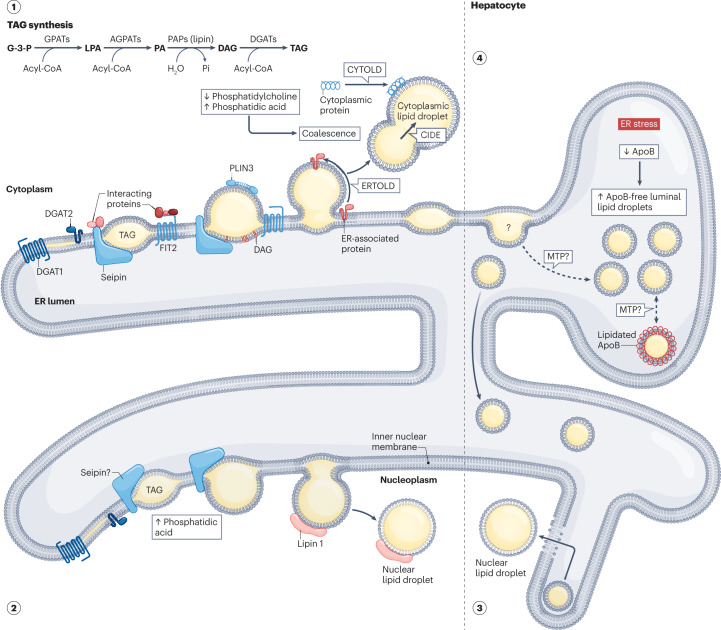
Fig. 1. Proposed mechanisms of eukaryotic lipid droplet biogenesis.
(1) Cytoplasmic lipid droplet biogenesis involves the synthesis, nucleation, cytoplasmic budding and growth of neutral lipids from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). DGAT1 and DGAT2 catalyse the formation of triacylglycerols (TAG; see inset for the biosynthesis pathway), which, once accumulated beyond 2.8–10.0 mol%, form lens structures at sites putatively defined by proteins, such as seipin and its interacting partners. Regulated by monolayer tension asymmetry, budding towards the cytosol might then occur spontaneously or be promoted by both proteins and lipids, including seipin, FIT2 or diacylglycerol (DAG). Ostwald ripening, coalescence, membrane bridges and both ERTOLD and CYTOLD proteins might then contribute to the growth of cytoplasmic lipid droplets. (2) De novo nuclear lipid droplet biogenesis is similar to cytoplasmic lipid droplet formation but occurs at the inner nuclear membrane. While the role of seipin remains controversial, increased phosphatidic acid levels are hypothesized to be pivotal. (3) In lipoprotein-secreting cells, nuclear lipid droplet biogenesis might also occur via the engulfment of luminal lipid droplets. During ER stress, degradation of ApoB but maintenance of MTP levels (top right) enable ApoB-free luminal lipid droplet accumulation in the ER lumen before entry into the nucleus through type I nucleoplasmic reticulum breakage. (4) Luminal lipid droplet biogenesis remains poorly characterized and confounded with VLDL biogenesis (lipidated ApoB represents nascent VLDL particles). Luminal lipid droplets are characterized as ApoB-free precursors. MTP might connect cytoplasmic lipid droplets with the formation of luminal lipid droplets and might also mediate the lipid transfer between luminal lipid droplets and lipidated ApoB. AGPAT, 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase; ApoB, apolipoprotein B-100; CIDE, cell death-inducing DFFA-like effector; CYTOLD, cytoplasm to lipid droplet targeting; DGAT, diacylglycerol transferase; ERTOLD, ER to lipid droplet targeting; FIT2, fat storage-inducing transmembrane protein 2; G-3-P, glycerol-3-phosphate; GPAT, glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase; LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; MTP, microsomal lipid transfer protein; PA, phosphatidic acid; PAP, phosphatidic acid phosphatase; Pi, inorganic phosphate; PLIN3, perilipin 3.