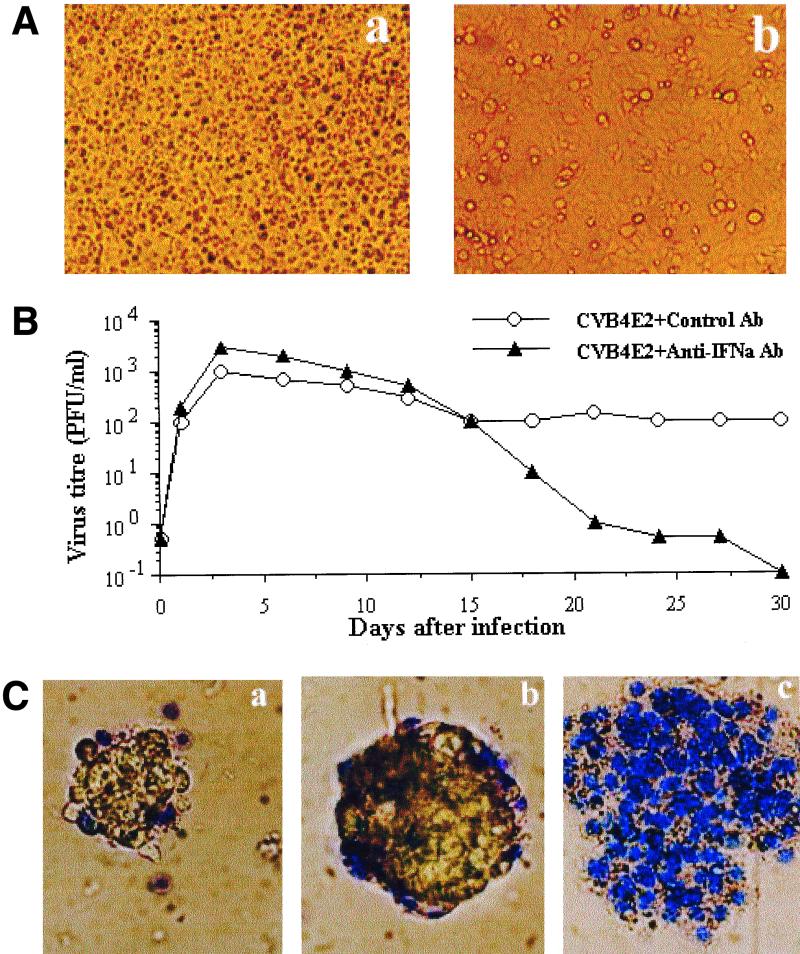
FIG. 8.
Antiviral activity of IFN-α produced by CVB4 E2-infected islets. (A) Antiviral activity of culture supernatant of CVB4 E2-infected islets. (a) Mock-infected islets. (b) CVB4 E2-infected islets. Human islets were cultured in 96-well plate inserts. Supernatants of islet cultures were UV irradiated before being added to HEp-2 cells and incubated for 24 h. HEp-2 cells were then washed and challenged with CVB4 E2 for 2 h and incubated for 24 h at 37°C. (B) Effect of anti-IFN-α neutralizing antibodies (Ab) on the susceptibility of human pancreatic islets to CVB4 E2. Islets cultured in 24-well plate inserts were infected with CVB4 E2 in the presence of anti-IFN-α neutralizing antibodies for 2 h. Islets were then washed and refed each 3 days with fresh medium supplemented with anti-IFN-α antibodies. The viral titers in culture supernatants were determined every 3 days of subculture by plaque infectivity assay on HEp-2 cell cultures. (C) Islet viability. (a) Mock-infected islets. (b) CVB4 E2-infected islets (c) CVB4 E2-infected islets cultured in the presence of anti-IFN-α neutralizing antibodies. The viability was assessed at 12 days after infection by using the trypan blue exclusion assay. These experiments were performed with islets from six brain-dead donors. Magnification, ×100.