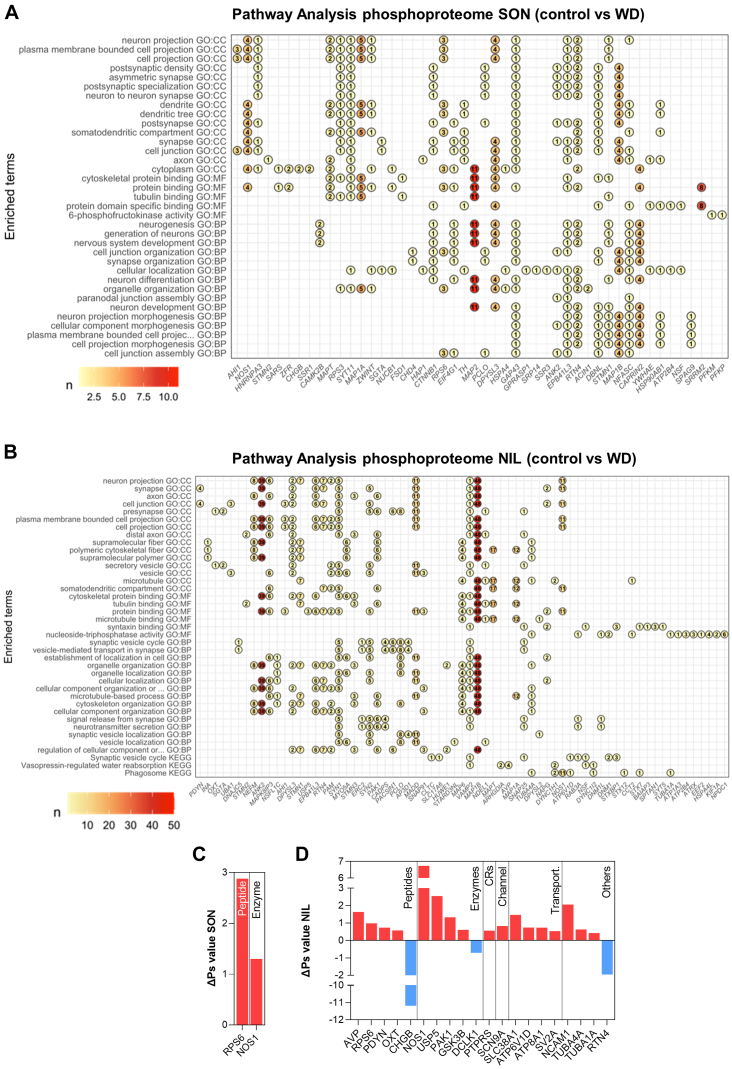
Fig. 4.
Pathway analyses and functional classification of the phosphoproteomes of supraoptic nucleus and neurointermediate lobe.A, pathway analysis of changes in the SON phosphoproteome as a result of water deprivation (WD) using GO and KEGG databases. Dot plot of up to 15 enriched terms retrieved for each category ranked according to PAdj value from top to bottom in increasing order. The top 10 proteins with most significant phosphorylation changes in a phosphosite are shown as a dot indicating the total number of phosphorylation events in that protein following WD. B, pathway analysis of changes in the NIL phosphoproteome as a result of WD using GO and KEGG databases. Dot plot of up to 15 enriched terms retrieved for each category ranked according to PAdj value from top to bottom in increasing order. The top 10 proteins with most significant phosphorylation changes in a phosphosite are shown as a dot indicating the total number of phosphorylation events in that protein following WD. C, ΔPs changes in the rat SON as a consequence of WD categorized according to their pharmacological classification or their function as a transcription factor. D, ΔPs changes in the rat NIL as a consequence of WD categorized according to their pharmacological classification or their function as a transcription factor. ΔPs, phosphorylation state change; GO, gene ontology; KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; NIL, neurointermediate lobe; SON, supraoptic nucleus.