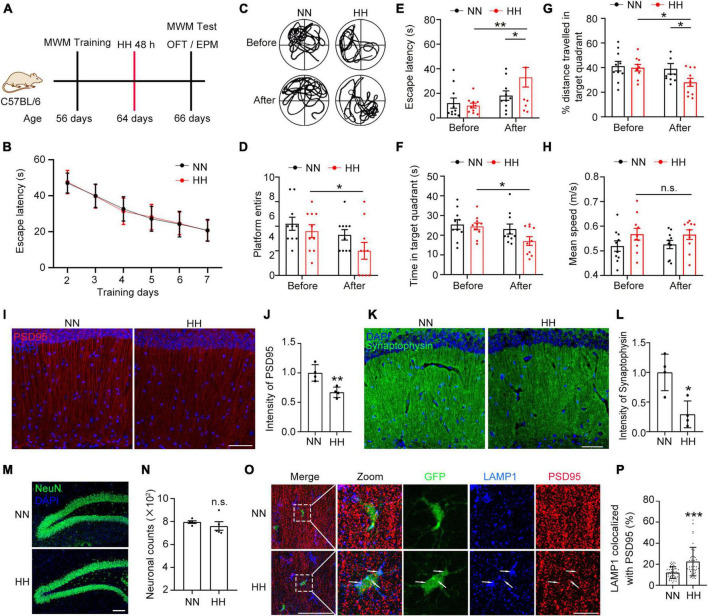
FIGURE 1.
Hypobaric hypoxia (HH) exposure induces synaptic loss in hippocampus and amnesia. (A) C57BL/6 mice were trained by MWM and exposed to simulated altitude of 7000 m for 48 h, and their memory changes were assessed by MWM and their anxiety was detected by OFT and EPM. n = 10. (B) Escape latency of two groups of mice before HH exposure during the training trails. (C) Trajectories of the mice in the MWM probe trails before and after HH exposure. (D) Number of times mice entered into the platform in probe trails. (E) Escape latency of mice reaching the target platform. (F) Residence time of mice in the target quadrant. (G) Ratio of distance traveled by mice in the target quadrant. (H) Mean swimming speed of mice during the probe trails. (I,J) Immunofluorescence labeling of the postsynaptic membrane marker PSD95 in excitatory neurons in the CA1 region of the hippocampus (interaural 1.62 mm), Scale bar = 50 μm, n = 4. (K,L) Immunofluorescent labeling of Synaptophysin, a presynaptic membrane marker of neurons in the CA1 region of the hippocampus (interaural 1.62 mm), Scale bar = 50 μm, n = 4. (M,N) Immunofluorescence labeling of NeuN in hippocampal DG area neurons and cell counting was performed by Image J software, Scale bar = 100 μm, n = 5. (O,P) Immunofluorescence labeling of PSD95 and the lysosomal marker LAMP1 in hippocampal CA1 region (interaural 1.74 mm) in CX3CR1-GFP mice after exposure to HH for 48 h, Scale bar = 10 μm (n = 43 in NN group, n = 48 in HH group. Brain sections from 6 mice of each group were stained, and 5–8 cells of each mouse were quantified). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and n.s. indicates no statistical differences.