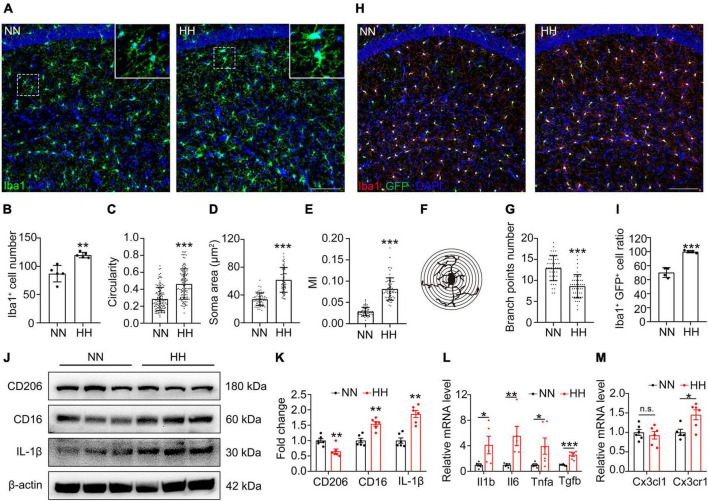
FIGURE 2.
Hypobaric hypoxia (HH) exposure induces CX3CL1/CX3CR1 signal activation and M1-type polarization of hippocampal microglia. (A) Immunofluorescence labeling of microglia/macrophage marker Iba1 in CA1, Scale bar = 100 μm. (B–G) Statistics of panel (A), including the number of Iba1+ cells [(B), n = 5], circularity [(C), n = 118, brain sections from 5 mice of each group were stained, and 23–24 cells of each mouse were quantified], soma area [(D), n = 61 or 68, brain sections from 5 mice of each group were stained, and 12–13 cells of each mouse were quantified], MI [(E), MI = soma area/arborization area, n = 62 or 64, brain sections from 5 mice of each group were stained, and 13–14 cells in CA1 region of each mouse were quantified] and number of branches [(F,G), n = 45, brain sections from 5 mice of each group were stained, and 9 cells of each mouse were quantified]. (H) Immunofluorescence labeling of microglia/macrophage marker Iba1 in CA1 region of CX3CR1-GFP mice, Scale bar = 100 μm. (I) Statistics of the ratio of Iba1+GFP+ cells in GFP + cells in panel (H), n = 4. (J,K) Western blot detection of CD206, CD16, and IL-1β levels in mouse hippocampus, n = 6. (L) qRT-PCR detection of the expression of inflammatory factors Il1b, Il6, Tnfa, and Tgfb in hippocampal tissue, n = 5. (M) qRT-PCR detection of Cx3cl1 and Cxcr1 expressions in hippocampal tissues, n = 6. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and n.s. indicates no statistical difference.