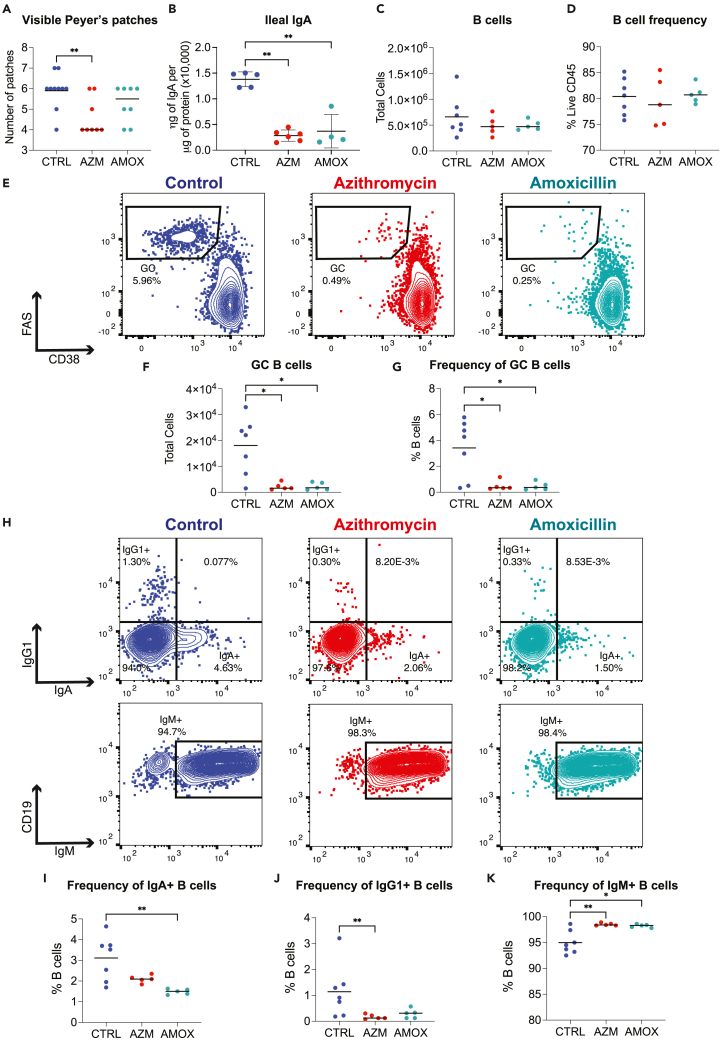
Figure 2.
Germinal center formation is altered at day of life 35 after early-life antibiotic exposure
At P35, mice were sacrificed, and Peyer’s patches were homogenized into single-cell suspensions and lymphocytes characterized using flow cytometry.
(A) Visible Peyer’s patches along the length of the small intestine were counted.
(B–D) IgA was quantitated in ileal tissue using an IgA-specific ELISA and normalized to total protein levels in the sample, as determined by BCA assay. Abundance and proportions of (C, D) B cells were assessed by flow cytometry.
(E–G) Representative flow cytometry plots of Peyer’s patch germinal center (GC) B cells and (F, G) summary data for GC B cells counts and frequency are plotted. Peyer’s patch single-cell suspensions were fixed and permeabilized after surface staining to permit intercellular staining of IgM, IgG1, and IgA.
(H–K) Representative flow plots for intracellular Ig staining. Summary plots for percent B cells positive for (I) IgA, (J) IgG1, or (K) IgM. All data shown are from a single representative experiment of three independent experiments; plot A shows the median, and all other plots show the mean value ±SEM; ∗ indicates p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.