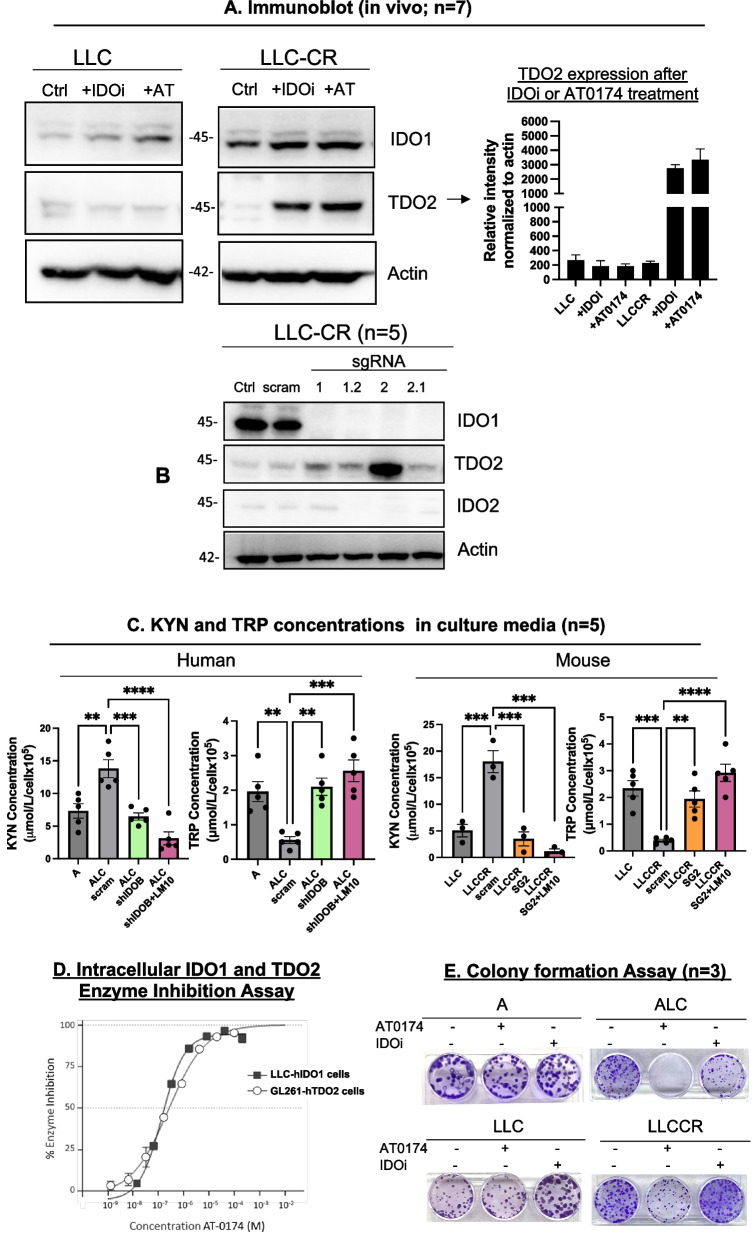
Fig. 3.
The compensatory role of IDO1 and TDO2 in cisplatin-resistant NSCLC. A Immunoblot of IDO1 and TDO2 from LLC vs. LLC-CR that were treated with either IDO1 inhibitor or dual inhibitor (AT-0174). The right panel indicated TDO2 relative intensity after IDO1 or IDO1/TDO2 blockage. B Immunoblot of IDO1, IDO2, and TDO2 expression in CRISPR-edited Ido1 knockout SG1 and SG2 tumors. Scram indicated gRNA control. C KYN (amino acid) and TRP concentrations were detected in human and mouse cell cultures. Blocking both IDO1 and TDO2 led to a significant reduction in KYN secretions with higher extracellular TRP concentrations. D IDO1 and TDO2 enzyme inhibition in response to AT-0174. LLC-hIDO1 or GL261-hTDO2 cells were incubated with AT-0174 for 24 h. The supernatant was collected and assayed for kynurenine activity by colorimetric assay. The inhibition potency (IC50 value) of AT-0174 on the IDO1 and TDO2 enzymes were calculated to be 0.17 µM and 0.25 µM, respectively. E Colony formations of human and mouse cell lines were determined in CS (A or LLC) vs. CR (ALC or LLC-CR) cells treated with 25 µM of AT-0174 or IDOi for 3 days and reseeded for 12 more days. Cell lines A and LLC are cisplatin-sensitive, and ALC and LLC-CR are cisplatin-resistant counterparts. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison analysis with *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005